This page was generated from unit-1.6-adaptivity/adaptivity.ipynb.
1.6 Error estimation & adaptive refinement¶
In this tutorial, we apply a Zienkiewicz-Zhu type error estimator and run an adaptive loop with these steps:
[1]:
from ngsolve import *
from ngsolve.webgui import Draw
from netgen.occ import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Geometry¶
The following geometry represents a heated chip embedded in another material that conducts away the heat.
[2]:
def MakeGeometryOCC():
base = Rectangle(1, 0.6).Face()
chip = MoveTo(0.5,0.15).Line(0.15,0.15).Line(-0.15,0.15).Line(-0.15,-0.15).Close().Face()
top = MoveTo(0.2,0.6).Rectangle(0.6,0.2).Face()
base -= chip
base.faces.name="base"
chip.faces.name="chip"
chip.faces.col=(1,0,0)
top.faces.name="top"
geo = Glue([base,chip,top])
geo.edges.name="default"
geo.edges.Min(Y).name="bot"
return OCCGeometry(geo, dim=2)
mesh = Mesh(MakeGeometryOCC().GenerateMesh(maxh=0.2))
Draw(mesh)
[2]:
BaseWebGuiScene
Spaces & forms¶
The problem is to find \(u\) in \(H_{0,D}^1\) satisfying
for all \(v\) in \(H_{0,D}^1\). We expect the solution to have singularities due to the nonconvex re-enrant angles and discontinuities in \(\lambda\).
[3]:
fes = H1(mesh, order=3, dirichlet=[1])
u, v = fes.TnT()
# one heat conductivity coefficient per sub-domain
lam = CoefficientFunction([1, 1000, 10])
a = BilinearForm(lam*grad(u)*grad(v)*dx)
# heat-source in inner subdomain
f = LinearForm(fes)
f = LinearForm(1*v*dx(definedon="chip"))
c = Preconditioner(a, type="multigrid", inverse="sparsecholesky")
gfu = GridFunction(fes)
Note that the linear system is not yet assembled above.
Solve¶
Since we must solve multiple times, we define a function to solve the boundary value problem, where assembly, update, and solve occurs.
[4]:
def SolveBVP():
fes.Update()
gfu.Update()
a.Assemble()
f.Assemble()
inv = CGSolver(a.mat, c.mat)
gfu.vec.data = inv * f.vec
[5]:
SolveBVP()
Draw(gfu);
Estimate¶
We implement a gradient-recovery-type error estimator. For this, we need an H(div) space for flux recovery. We must compute the flux of the computed solution and interpolate it into this H(div) space.
[6]:
space_flux = HDiv(mesh, order=2)
gf_flux = GridFunction(space_flux, "flux")
flux = lam * grad(gfu)
gf_flux.Set(flux)
Element-wise error estimator: On each element \(T\), set
where \(u_h\) is the computed solution gfu and \(I_h\) is the interpolation performed by Set in NGSolve.
[7]:
err = 1/lam*(flux-gf_flux)*(flux-gf_flux)
Draw(err, mesh, 'error_representation')
[7]:
BaseWebGuiScene
[8]:
eta2 = Integrate(err, mesh, VOL, element_wise=True)
print(eta2)
5.80014e-10
7.49183e-08
8.51912e-06
4.54368e-10
8.33308e-08
4.83986e-09
3.08064e-07
7.02005e-10
1.1091e-08
3.03261e-08
1.0408e-07
2.48804e-07
7.10938e-08
8.58958e-07
7.75911e-06
1.01521e-06
6.85467e-08
7.87624e-06
2.05199e-06
2.25556e-08
1.65616e-07
6.07265e-08
1.74824e-06
1.18772e-06
3.46568e-07
2.52966e-06
1.46647e-09
1.88656e-06
1.17887e-06
4.09713e-08
1.57525e-07
1.60365e-09
1.92225e-08
1.9544e-08
1.14778e-09
9.56943e-10
6.7901e-09
8.51976e-10
1.44089e-10
9.55771e-09
The above values, one per element, lead us to identify elements which might have large error.
Mark¶
We mark elements with large error estimator for refinement.
[9]:
maxerr = max(eta2)
print ("maxerr = ", maxerr)
for el in mesh.Elements():
mesh.SetRefinementFlag(el, eta2[el.nr] > 0.25*maxerr)
# see below for vectorized alternative
maxerr = 8.519121326541049e-06
Refine & solve again¶
Refine marked elements:
[10]:
mesh.Refine()
SolveBVP()
Draw(gfu)
[10]:
BaseWebGuiScene
Automate the above steps¶
[11]:
l = [] # l = list of estimated total error
def CalcError():
# compute the flux:
space_flux.Update()
gf_flux.Update()
flux = lam * grad(gfu)
gf_flux.Set(flux)
# compute estimator:
err = 1/lam*(flux-gf_flux)*(flux-gf_flux)
eta2 = Integrate(err, mesh, VOL, element_wise=True)
maxerr = max(eta2)
l.append ((fes.ndof, sqrt(sum(eta2))))
print("ndof =", fes.ndof, " maxerr =", maxerr)
# mark for refinement (vectorized alternative)
mesh.ngmesh.Elements2D().NumPy()["refine"] = eta2.NumPy() > 0.25*maxerr
[12]:
CalcError()
mesh.Refine()
ndof = 328 maxerr = 5.0385892733977e-06
Run the adaptive loop¶
[13]:
level = 0
while fes.ndof < 50000:
SolveBVP()
level = level + 1
if level%5 == 0:
print('adaptive step #', level)
Draw(gfu)
CalcError()
mesh.Refine()
ndof = 583 maxerr = 2.0247198934825063e-06
ndof = 997 maxerr = 8.0374929330418e-07
ndof = 1492 maxerr = 3.1888429487698495e-07
ndof = 2143 maxerr = 1.264974505886916e-07
adaptive step # 5
ndof = 2917 maxerr = 5.01634985327537e-08
ndof = 3775 maxerr = 1.988922745586041e-08
ndof = 4651 maxerr = 8.08369538279698e-09
ndof = 5440 maxerr = 3.86423125252989e-09
ndof = 6211 maxerr = 1.8513183508753528e-09
adaptive step # 10
ndof = 6910 maxerr = 8.88018609108649e-10
ndof = 7456 maxerr = 4.2622762648173923e-10
ndof = 8263 maxerr = 2.0464796527367645e-10
ndof = 9433 maxerr = 9.827590625263762e-11
ndof = 10495 maxerr = 4.719861824266745e-11
adaptive step # 15
ndof = 12130 maxerr = 2.2668856545775322e-11
ndof = 13675 maxerr = 1.0887894643432407e-11
ndof = 15259 maxerr = 5.229541399463823e-12
ndof = 18055 maxerr = 2.5117726640897505e-12
ndof = 20347 maxerr = 1.2064449409699737e-12
adaptive step # 20
ndof = 23761 maxerr = 5.79460999395933e-13
ndof = 27262 maxerr = 2.7832639279306787e-13
ndof = 31426 maxerr = 1.3367946296920183e-13
ndof = 37588 maxerr = 6.420965229814459e-14
ndof = 43645 maxerr = 3.0839098645895766e-14
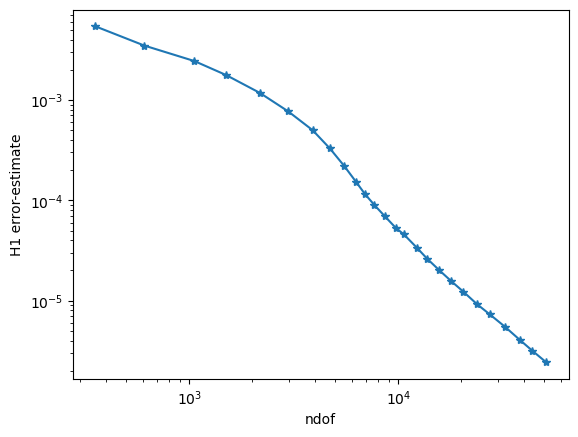
Plot history of adaptive convergence¶
[14]:
plt.yscale('log')
plt.xscale('log')
plt.xlabel("ndof")
plt.ylabel("H1 error-estimate")
ndof,err = zip(*l)
plt.plot(ndof,err, "-*")
plt.ion()
plt.show()