This page was generated from unit-2.8-DG/DG.ipynb.
2.8 Discontinuous Galerkin Methods¶
Use discontinuous finite element spaces to solve PDEs.
Allows upwind-stabilization for convection-dominated problems
Requires additional jump terms for consistency
Interior penalty DG form for \(-\Delta u\):
with jump-term over facets:
and averaging operator
DG form for \(\Div (b u)\), where \(b\) is the given wind:
[1]:
from ngsolve import *
from ngsolve.webgui import Draw
from netgen.geom2d import unit_square
mesh = Mesh(unit_square.GenerateMesh(maxh=0.3))
Generate Mesh from spline geometry
Boundary mesh done, np = 12
CalcLocalH: 12 Points 0 Elements 0 Surface Elements
Meshing domain 1 / 1
load internal triangle rules
Surface meshing done
Edgeswapping, topological
Smoothing
Split improve
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Split improve
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Split improve
Combine improve
Smoothing
Update mesh topology
Update clusters
The space is responsible for allocating the matrix graph. Tell it that it should reserve entries for the coupling terms:
[2]:
order=4
fes = L2(mesh, order=order, dgjumps=True)
u,v = fes.TnT()
Every facet has a master element. The value from the other element is referred to via the Other() operator:
[3]:
jump_u = u-u.Other()
jump_v = v-v.Other()
n = specialcf.normal(2)
mean_dudn = 0.5*n * (grad(u)+grad(u.Other()))
mean_dvdn = 0.5*n * (grad(v)+grad(v.Other()))
Integrals on facets are computed by setting skeleton=True. * dx(skeleton=True) iterates over all internal faces * ds(skeleton=True) iterates over all boundary faces
[4]:
alpha = 4
h = specialcf.mesh_size
a = BilinearForm(fes)
diffusion = grad(u)*grad(v) * dx \
+alpha*order**2/h*jump_u*jump_v * dx(skeleton=True) \
+(-mean_dudn*jump_v-mean_dvdn*jump_u) * dx(skeleton=True) \
+alpha*order**2/h*u*v * ds(skeleton=True) \
+(-n*grad(u)*v-n*grad(v)*u)* ds(skeleton=True)
a += diffusion
a.Assemble()
assemble VOL element 24/24
assemble inner facet 42/42
[4]:
<ngsolve.comp.BilinearForm at 0x7fe590971830>
[5]:
f = LinearForm(fes)
f += 1*v*dx
f.Assemble()
[5]:
<ngsolve.comp.LinearForm at 0x7fe59096a2f0>
assemble VOL element 24/24
[6]:
gfu = GridFunction(fes, name="uDG")
gfu.vec.data = a.mat.Inverse() * f.vec
Draw (gfu)
call pardiso ... done
[6]:
BaseWebGuiScene
DG requires a lot of additional matrix entries:
[7]:
print ("a nze:", a.mat.nze)
fes2 = L2(mesh, order=order)
a2 = BilinearForm(fes2)
a2 += u*v*dx
a2.Assemble()
print ("a2 nze:", a2.mat.nze)
a nze: 18900
a2 nze: 5400
assemble VOL element 24/24
Next we are solving a convection-diffusion problem:
[8]:
alpha = 4
h = specialcf.mesh_size
The IfPos checks whether the first argument is positive. Then it returns the second one, else the third one. This is used to define the upwind flux. The check is performed in every integration-point on the skeleton:
[9]:
b = CoefficientFunction( (20,5) )
uup = IfPos(b*n, u, u.Other())
convection = -b * u * grad(v)*dx + b*n*uup*jump_v * dx(skeleton=True)
acd = BilinearForm(fes)
acd += diffusion + convection
[10]:
acd.Assemble()
assemble VOL element 24/24
assemble inner facet 42/42
[10]:
<ngsolve.comp.BilinearForm at 0x7fe578a81af0>
[11]:
gfu = GridFunction(fes)
gfu.vec.data = acd.mat.Inverse(freedofs=fes.FreeDofs(),inverse="umfpack") * f.vec
Draw (gfu)
call umfpack ... done
[11]:
BaseWebGuiScene
Hybrid Discontinuous Galerkin methods¶
use additionally the hybrid facet variable on the skeleton:
the jump-term is now replaced by the difference \(u - \widehat u\).
No additional matrix entries across elements are produced. Dirichlet boundary conditions are set as usual to the facet variable:
[12]:
order=4
V = L2(mesh, order=order)
F = FacetFESpace(mesh, order=order, dirichlet="bottom|left|right|top")
fes = FESpace([V,F])
u,uhat = fes.TrialFunction()
v,vhat = fes.TestFunction()
Now, the jump is the difference between element-term and facet-term:
[13]:
jump_u = u-uhat
jump_v = v-vhat
[14]:
alpha = 4
condense = True
h = specialcf.mesh_size
n = specialcf.normal(mesh.dim)
a = BilinearForm(fes, condense=condense)
dS = dx(element_boundary=True)
a += grad(u)*grad(v)*dx + \
alpha*order**2/h*jump_u*jump_v*dS + \
(-grad(u)*n*jump_v - grad(v)*n*jump_u)*dS
b = CoefficientFunction( (20,1) )
uup = IfPos(b*n, u, uhat)
a += -b * u * grad(v)*dx + b*n*uup*jump_v *dS
a.Assemble()
f = LinearForm(fes)
f += 1*v*dx
f.Assemble()
gfu = GridFunction(fes)
print ("A non-zero elements:", a.mat.nze)
assemble VOL element 24/24
A non-zero elements: 4650
assemble VOL element 24/24
[15]:
if not condense:
inv = a.mat.Inverse(fes.FreeDofs(), "umfpack")
gfu.vec.data = inv * f.vec
else:
f.vec.data += a.harmonic_extension_trans * f.vec
inv = a.mat.Inverse(fes.FreeDofs(True), "umfpack")
gfu.vec.data = inv * f.vec
gfu.vec.data += a.harmonic_extension * gfu.vec
gfu.vec.data += a.inner_solve * f.vec
Draw (gfu.components[0], mesh, "u-HDG")
call umfpack ... done
[15]:
BaseWebGuiScene
Projected Jumps¶
The polynomial order of the facet-space can be reduced by one by inserting an \(L_2\)-projection into the penalty term. This can be implemented by keeping the highest order basis functions of the facet space discontinuous, see Lehrenfeld-Schöberl: High order exactly divergence-free Hybrid Discontinuous Galerkin Methods for unsteady incompressible flows:
This is achieved by setting the flag highest_order_dc=True in the FacetFESpace. The number of matrix entries is reduced, while the order of convergence is preserved. This trick does not work in the case of significant convection.
[16]:
order=4
V = L2(mesh, order=order)
F = FacetFESpace(mesh, order=order, dirichlet="bottom|left|right|top", \
highest_order_dc=True)
fes = FESpace([V,F])
u,uhat = fes.TrialFunction()
v,vhat = fes.TestFunction()
jump_u = u-uhat
jump_v = v-vhat
alpha = 2
h = specialcf.mesh_size
n = specialcf.normal(mesh.dim)
a = BilinearForm(fes, condense=True)
dS = dx(element_boundary=True)
a += grad(u)*grad(v)*dx + \
alpha*(order+1)**2/h*jump_u*jump_v*dS + \
(-grad(u)*n*jump_v - grad(v)*n*jump_u)*dS
a.Assemble()
f = LinearForm(fes)
f += 1*v*dx
f.Assemble()
gfu = GridFunction(fes)
f.vec.data += a.harmonic_extension_trans * f.vec
inv = a.mat.Inverse(fes.FreeDofs(True), "sparsecholesky")
gfu.vec.data = inv * f.vec
gfu.vec.data += a.harmonic_extension * gfu.vec
gfu.vec.data += a.inner_solve * f.vec
Draw (gfu.components[0], mesh, "u-HDG")
print ("A non-zero elements:", a.mat.nze)
assemble VOL element 24/24
assemble VOL element 24/24
A non-zero elements: 2976
Remarks on sparsity pattern in NGSolve¶
Remark 1: The sparsity pattern is set up a-priorily¶
The sparsity pattern of a sparse matrix in NGSolve is independent of its entries (it’s set up a-priorily).
We can have “nonzero” entries that have the value 0
Below we show the reserved memory for the sparse matrix and the (numerically) non-zero entries in this sparse matrix.
[17]:
fes2 = L2(mesh, order=order, dgjumps=True)
u,v=fes2.TnT()
a3 = BilinearForm(fes2)
a3 += u*v*dx + (u+u.Other())*v*dx(skeleton=True)
a3.Assemble()
assemble VOL element 24/24
[17]:
<ngsolve.comp.BilinearForm at 0x7fe5ccb2acf0>
assemble inner facet 42/42
[18]:
import scipy.sparse as sp
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (12, 12)
A = sp.csr_matrix(a3.mat.CSR())
fig = plt.figure(); ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121); ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122)
ax1.set_xlabel("numerically non-zero"); ax1.spy(A)
ax2.set_xlabel("reserved entries (potentially non-zero)"); ax2.spy(A,precision=-1)
plt.show()
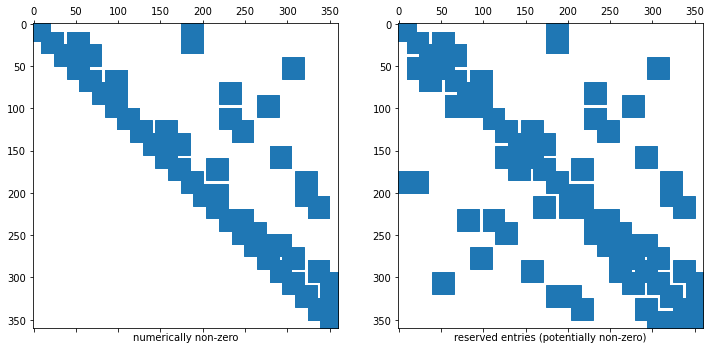
Remark 2: Sparsity pattern with and without dgjumps=True is different¶
[19]:
a1 = BilinearForm(L2(mesh, order=order, dgjumps=False)); a1.Assemble()
a2 = BilinearForm(L2(mesh, order=order, dgjumps=True)); a2.Assemble()
A1 = sp.csr_matrix(a1.mat.CSR())
A2 = sp.csr_matrix(a2.mat.CSR())
fig = plt.figure(); ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121); ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122)
ax1.set_xlabel("dgjumps=False"); ax1.spy(A1,precision=-1)
ax2.set_xlabel("dgjumps=True"); ax2.spy(A2,precision=-1)
plt.show()
used dof inconsistency
(silence this warning by setting BilinearForm(...check_unused=False) )
used dof inconsistency
(silence this warning by setting BilinearForm(...check_unused=False) )
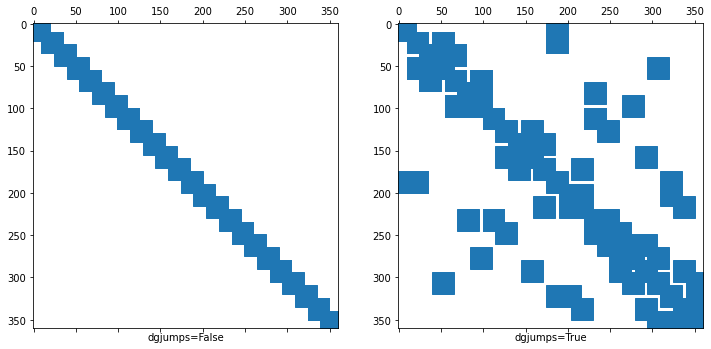
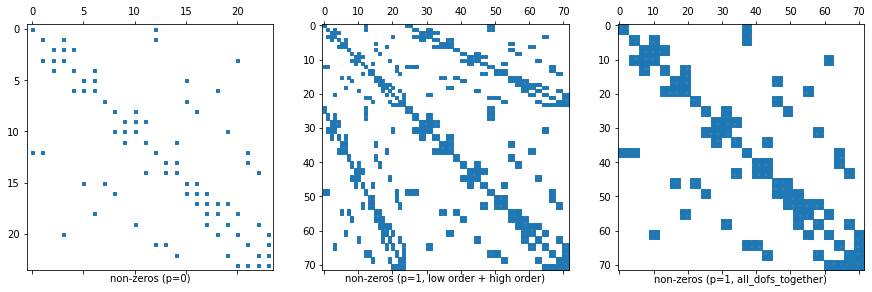
Remark 3: Dof numbering of higher order FESpaces¶
In
NGSolveFESpaces typically have a numbering where the first block of dofs corresponds to a low order subspace (which is convenient for iterative solvers).For L2 this means that the first dofs correspond to the constants on elements.
You can turn this behavior off for some spaces, e.g. for L2 by adding the flag
all_dofs_together.
We demonstrate this in the next comparison:
[20]:
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (15, 15)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = [fig.add_subplot(131), fig.add_subplot(132), fig.add_subplot(133)]
for i, (order, all_dofs_together, label) in enumerate([(0,False, "non-zeros (p=0)"),
(1,False,"non-zeros (p=1, low order + high order)"),
(1,True,"non-zeros (p=1, all_dofs_together)")]):
a = BilinearForm(L2(mesh,order=order,dgjumps=True,all_dofs_together=all_dofs_together))
a.Assemble()
ax[i].spy(sp.csr_matrix(a.mat.CSR()),markersize=3,precision=-1)
ax[i].set_xlabel(label)
used dof inconsistency
(silence this warning by setting BilinearForm(...check_unused=False) )
used dof inconsistency
(silence this warning by setting BilinearForm(...check_unused=False) )
used dof inconsistency
(silence this warning by setting BilinearForm(...check_unused=False) )
[ ]: