This page was generated from unit-2.1.3-bddc/bddc.ipynb.
2.1.3 Element-wise BDDC Preconditioner¶
The element-wise BDDC (Balancing Domain Decomposition preconditioner with Constraints) preconditioner in NGSolve is a good general purpose preconditioner that works well both in the shared memory parallel mode as well as in distributed memory mode. In this tutorial, we discuss this preconditioner, related built-in options, and customization from python.
Let us start with a simple description of the element-wise BDDC in the context of Lagrange finite element space \(V\). Here the BDDC preconditoner is constructed on an auxiliary space \(\widetilde{V}\) obtained by connecting only element vertices (leaving edge and face shape functions discontinuous). Although larger, the auxiliary space allows local elimination of edge and face variables. Hence an analogue of the original matrix \(A\) on this space, named \(\widetilde A\), is less expensive to invert. This inverse is used to construct a preconditioner for \(A\) as follows:
Here, \(R\) is the averaging operator for the discontinous edge and face variables.
To construct a general purpose BDDC preconditioner, NGSolve generalizes this idea to all its finite element spaces by a classification of degrees of freedom. Dofs are classified into (condensable) LOCAL_DOFs that we saw in 1.4 and a remainder that includes these types:
WIREBASKET_DOFINTERFACE_DOFThe original finite element space \(V\) is obtained by requiring conformity of both the above types of dofs, while the auxiliary space \(\widetilde{V}\) is obtained by requiring conformity of WIREBASKET_DOFs only.
Here is a figure of a typical function in the default \(\widetilde{V}\) (and the code to generate this is at the end of this tutorial) when \(V\) is the Lagrange space:
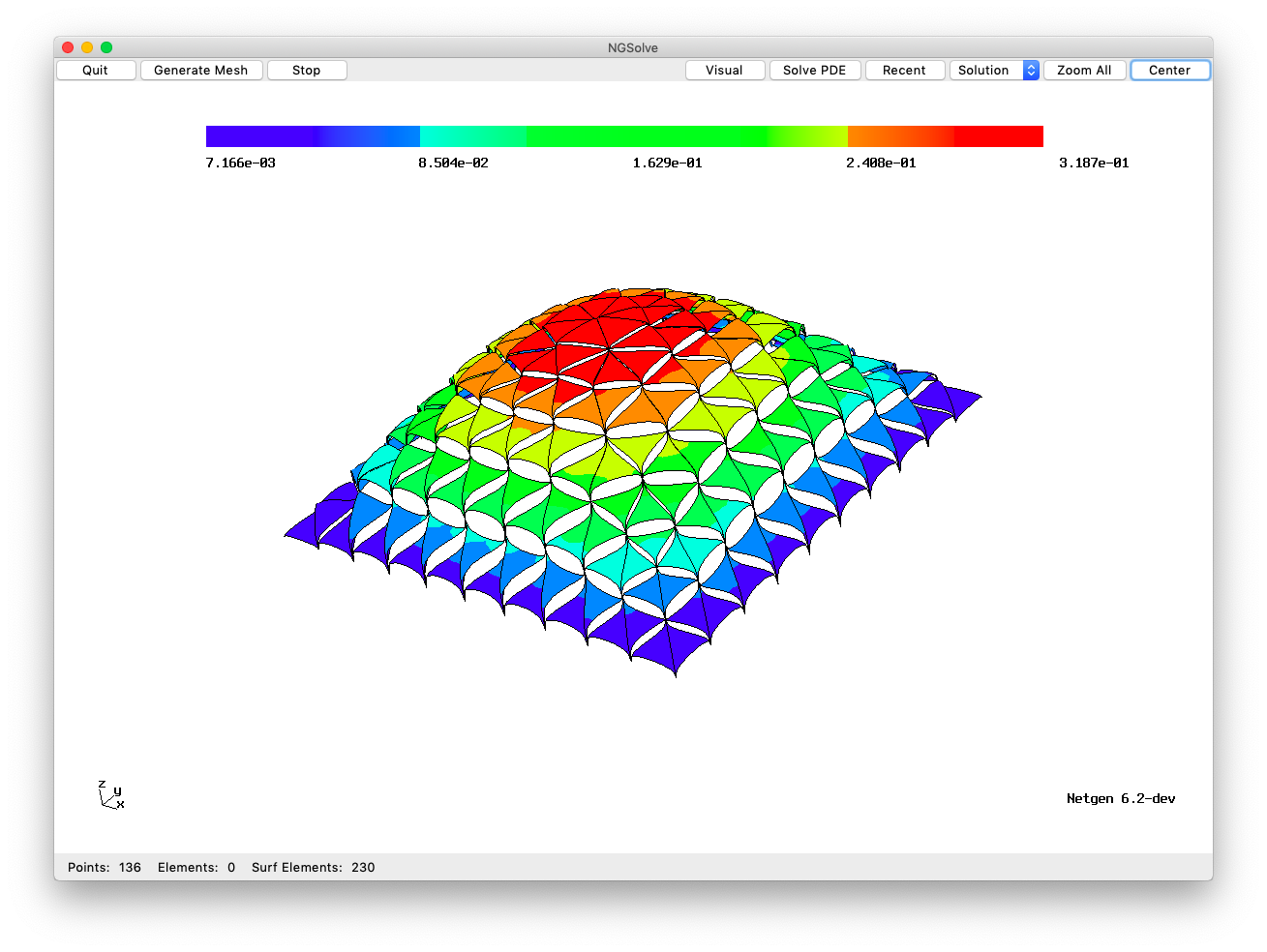
[1]:
from ngsolve import *
from ngsolve.webgui import Draw
from ngsolve.la import EigenValues_Preconditioner
from netgen.csg import unit_cube
from netgen.geom2d import unit_square
SetHeapSize(100*1000*1000)
[2]:
mesh = Mesh(unit_cube.GenerateMesh(maxh=0.5))
# mesh = Mesh(unit_square.GenerateMesh(maxh=0.5))
Start Findpoints
main-solids: 1
Found points 8
Analyze spec points
Find edges
12 edges found
Check intersecting edges
CalcLocalH: 20 Points 0 Elements 0 Surface Elements
Start Findpoints
Analyze spec points
Find edges
12 edges found
Check intersecting edges
Start Findpoints
Analyze spec points
Find edges
12 edges found
Check intersecting edges
Surface 1 / 6
load internal triangle rules
Surface meshing done
0 illegal triangles
Optimize Surface
Edgeswapping, topological
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
6 elements, 20 points
Surface 2 / 6
Surface meshing done
0 illegal triangles
Optimize Surface
Edgeswapping, topological
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
6 elements, 20 points
Surface 3 / 6
Surface meshing done
0 illegal triangles
Optimize Surface
Edgeswapping, topological
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
6 elements, 20 points
Surface 4 / 6
Surface meshing done
0 illegal triangles
Optimize Surface
Edgeswapping, topological
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
6 elements, 20 points
Surface 5 / 6
Surface meshing done
0 illegal triangles
Optimize Surface
Edgeswapping, topological
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
6 elements, 20 points
Surface 6 / 6
Surface meshing done
0 illegal triangles
Optimize Surface
Edgeswapping, topological
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
6 elements, 20 points
SplitSeparateFaces
Check subdomain 1 / 1
Meshing subdomain 1 of 1
Use internal rules
Delaunay meshing
number of points: 20
blockfill local h
number of points: 29
Points: 29
Elements: 142
Tree data entries per element: 1.40845
Tree nodes per element: 0.0211268
SwapImprove
SwapImprove
SwapImprove
SwapImprove
0 degenerated elements removed
Remove intersecting
Remove outer
29 points, 64 elements
start tetmeshing
Use internal rules
Success !
29 points, 83 elements
Remove Illegal Elements
Volume Optimization
CombineImprove
ImproveMesh
SplitImprove
ImproveMesh
SwapImprove
SwapImprove2
ImproveMesh
CombineImprove
ImproveMesh
SplitImprove
ImproveMesh
SwapImprove
SwapImprove2
ImproveMesh
CombineImprove
ImproveMesh
SplitImprove
ImproveMesh
SwapImprove
SwapImprove2
ImproveMesh
Update mesh topology
Update clusters
Built-in options¶
Let us define a simple function to study how the spectrum of the preconditioned matrix changes with various options.
Effect of condensation¶
[3]:
def TestPreconditioner (p, condense=False, **args):
fes = H1(mesh, order=p, **args)
u,v = fes.TnT()
a = BilinearForm(fes, eliminate_internal=condense)
a += grad(u)*grad(v)*dx + u*v*dx
c = Preconditioner(a, "bddc")
a.Assemble()
return EigenValues_Preconditioner(a.mat, c.mat)
[4]:
lams = TestPreconditioner(5)
print (lams[0:3], "...\n", lams[-3:])
assemble VOL element 63/63
call wirebasket inverse ( with 136 free dofs out of 1576 )
has inverse
1.00228
1.0408
1.13959
...
7.43053
7.57517
7.66553
eigen-it 0/200
eigen-it 1/200
eigen-it 2/200
eigen-it 3/200
eigen-it 4/200
eigen-it 5/200
eigen-it 6/200
eigen-it 7/200
eigen-it 8/200
eigen-it 9/200
eigen-it 10/200
eigen-it 11/200
eigen-it 12/200
eigen-it 13/200
eigen-it 14/200
eigen-it 15/200
eigen-it 16/200
eigen-it 17/200
eigen-it 18/200
eigen-it 19/200
eigen-it 20/200
eigen-it 21/200
eigen-it 22/200
eigen-it 23/200
eigen-it 24/200
Here is the effect of static condensation on the BDDC preconditioner.
[5]:
lams = TestPreconditioner(5, condense=True)
print (lams[0:3], "...\n", lams[-3:])
assemble VOL element 63/63
call wirebasket inverse ( with 136 free dofs out of 1576 )
has inverse
1.00137
1.03997
1.11644
...
6.92348
7.01741
7.29845
eigen-it 0/200
eigen-it 1/200
eigen-it 2/200
eigen-it 3/200
eigen-it 4/200
eigen-it 5/200
eigen-it 6/200
eigen-it 7/200
eigen-it 8/200
eigen-it 9/200
eigen-it 10/200
eigen-it 11/200
eigen-it 12/200
eigen-it 13/200
eigen-it 14/200
eigen-it 15/200
eigen-it 16/200
eigen-it 17/200
eigen-it 18/200
eigen-it 19/200
eigen-it 20/200
eigen-it 21/200
eigen-it 22/200
eigen-it 23/200
Tuning the auxiliary space¶
Next, let us study the effect of a few built-in flags for finite element spaces that are useful for tweaking the behavior of the BDDC preconditioner. The effect of these flags varies in two (2D) and three dimensions (3D), e.g.,
wb_fulledges=True: This option keeps all edge-dofs conforming (i.e. they are markedWIREBASKET_DOFs). This option is only meaningful in 3D. If used in 2D, the preconditioner becomes a direct solver.wb_withedges=True: This option keeps only the first edge-dof conforming (i.e., the first edge-dof is markedWIREBASKET_DOFand the remaining edge-dofs are markedINTERFACE_DOFs).
The complete situation is a bit more complex due to the fact these options can take the three values True, False, or Undefined, the two options can be combined, and the space dimension can be 2 or 3. The default value of these flags in NGSolve is Undefined. Here is a table with the summary of the effect of these options:
wb_fulledges |
wb_withedges |
2D |
3D |
|---|---|---|---|
True |
any value |
all |
all |
False/Undefined |
Undefined |
none |
first |
False/Undefined |
False |
none |
none |
False/Undefined |
True |
first |
first |
An entry \(X \in\) {all, none, first} of the last two columns is to be read as follows: \(X\) of the edge-dofs is(are) WIREBASKET_DOF(s).
Here is an example of the effect of one of these flag values.
[6]:
lams = TestPreconditioner(5, condense=True,
wb_withedges=False)
print (lams[0:3], "...\n", lams[-3:])
assemble VOL element 63/63
call wirebasket inverse ( with 28 free dofs out of 1576 )
has inverse
1.00412
1.09464
1.33392
...
31.0804
33.0369
33.6461
eigen-it 0/200
eigen-it 1/200
eigen-it 2/200
eigen-it 3/200
eigen-it 4/200
eigen-it 5/200
eigen-it 6/200
eigen-it 7/200
eigen-it 8/200
eigen-it 9/200
eigen-it 10/200
eigen-it 11/200
eigen-it 12/200
eigen-it 13/200
eigen-it 14/200
eigen-it 15/200
eigen-it 16/200
eigen-it 17/200
eigen-it 18/200
eigen-it 19/200
eigen-it 20/200
eigen-it 21/200
eigen-it 22/200
eigen-it 23/200
eigen-it 24/200
eigen-it 25/200
eigen-it 26/200
eigen-it 27/200
eigen-it 28/200
eigen-it 29/200
eigen-it 30/200
eigen-it 31/200
Clearly, when moving from the default case (where the first of the edge dofs are wire basket dofs) to the case (where none of the edge dofs are wire basket dofs), the conditioning became less favorable.
Customize¶
From within python, we can change the types of degrees of freedom of finite element spaces, thus affecting the behavior of the BDDC preconditioner.
To depart from the default and commit the first two edge dofs to wire basket, we perform the next steps:
[7]:
fes = H1(mesh, order=10)
u,v = fes.TnT()
for ed in mesh.edges:
dofs = fes.GetDofNrs(ed)
for d in dofs:
fes.SetCouplingType(d, COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF)
# Set the first two edge dofs to be conforming
fes.SetCouplingType(dofs[0], COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF)
fes.SetCouplingType(dofs[1], COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF)
a = BilinearForm(fes, eliminate_internal=True)
a += grad(u)*grad(v)*dx + u*v*dx
c = Preconditioner(a, "bddc")
a.Assemble()
lams=EigenValues_Preconditioner(a.mat, c.mat)
max(lams)/min(lams)
assemble VOL element 63/63
call wirebasket inverse ( with 244 free dofs out of 11476 )
has inverse
eigen-it 0/200
eigen-it 1/200
eigen-it 2/200
eigen-it 3/200
eigen-it 4/200
eigen-it 5/200
eigen-it 6/200
eigen-it 7/200
eigen-it 8/200
eigen-it 9/200
eigen-it 10/200
eigen-it 11/200
eigen-it 12/200
eigen-it 13/200
eigen-it 14/200
eigen-it 15/200
eigen-it 16/200
eigen-it 17/200
eigen-it 18/200
eigen-it 19/200
eigen-it 20/200
eigen-it 21/200
eigen-it 22/200
eigen-it 23/200
eigen-it 24/200
eigen-it 25/200
eigen-it 26/200
eigen-it 27/200
eigen-it 28/200
eigen-it 29/200
[7]:
18.178677170664105
This is a slight improvement from the default.
[8]:
lams = TestPreconditioner (10, condense=True)
max(lams)/min(lams)
assemble VOL element 63/63
call wirebasket inverse ( with 136 free dofs out of 11476 )
has inverse
[8]:
27.35966282226837
eigen-it 0/200
eigen-it 1/200
eigen-it 2/200
eigen-it 3/200
eigen-it 4/200
eigen-it 5/200
eigen-it 6/200
eigen-it 7/200
eigen-it 8/200
eigen-it 9/200
eigen-it 10/200
eigen-it 11/200
eigen-it 12/200
eigen-it 13/200
eigen-it 14/200
eigen-it 15/200
eigen-it 16/200
eigen-it 17/200
eigen-it 18/200
eigen-it 19/200
eigen-it 20/200
eigen-it 21/200
eigen-it 22/200
eigen-it 23/200
eigen-it 24/200
eigen-it 25/200
eigen-it 26/200
eigen-it 27/200
eigen-it 28/200
eigen-it 29/200
eigen-it 30/200
Combine BDDC with AMG for large problems¶
coarsetype=h1amg flag, we can ask BDDC to replace \({\,\widetilde{A}\,}^{-1}\) by an Algebraic MultiGrid (AMG) preconditioner. Since NGSolve’s h1amg is well-suitedwb_withedges=False to ensure that \(\widetilde{A}\) is made solely with vertex unknowns.[9]:
p = 5
mesh = Mesh(unit_cube.GenerateMesh(maxh=0.05))
fes = H1(mesh, order=p, dirichlet="left|bottom|back",
wb_withedges=False)
print("NDOF = ", fes.ndof)
u,v = fes.TnT()
a = BilinearForm(fes)
a += grad(u)*grad(v)*dx
f = LinearForm(fes)
f += v*dx
with TaskManager():
pre = Preconditioner(a, "bddc", coarsetype="h1amg")
a.Assemble()
f.Assemble()
gfu = GridFunction(fes)
solvers.CG(mat=a.mat, rhs=f.vec, sol=gfu.vec,
pre=pre, maxsteps=500)
Draw(gfu)
Start Findpoints
main-solids: 1
Found points 8
Analyze spec points
Find edges
12 edges found
Check intersecting edges
CalcLocalH: 236 Points 0 Elements 0 Surface Elements
Start Findpoints
Analyze spec points
Find edges
12 edges found
Check intersecting edges
Start Findpoints
Analyze spec points
Find edges
12 edges found
Check intersecting edges
Surface 1 / 6
Surface meshing done
0 illegal triangles
Optimize Surface
Edgeswapping, topological
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
922 elements, 658 points
Surface 2 / 6
Surface meshing done
0 illegal triangles
Optimize Surface
Edgeswapping, topological
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
964 elements, 1101 points
Surface 3 / 6
Surface meshing done
0 illegal triangles
Optimize Surface
Edgeswapping, topological
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
970 elements, 1547 points
Surface 4 / 6
Surface meshing done
0 illegal triangles
Optimize Surface
Edgeswapping, topological
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
946 elements, 1981 points
Surface 5 / 6
Surface meshing done
0 illegal triangles
Optimize Surface
Edgeswapping, topological
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
970 elements, 2427 points
Surface 6 / 6
Surface meshing done
0 illegal triangles
Optimize Surface
Edgeswapping, topological
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Combine improve
Smoothing
970 elements, 2873 points
SplitSeparateFaces
Check subdomain 1 / 1
Meshing subdomain 1 of 1
Use internal rules
Delaunay meshing
number of points: 2827
blockfill local h
number of points: 12268
Points: 12268
Elements: 71430
Tree data entries per element: 1.69537
Tree nodes per element: 0.0338933
SwapImprove
SwapImprove
SwapImprove
SwapImprove
0 degenerated elements removed
Remove intersecting
Remove outer
12268 points, 65567 elements
start tetmeshing
Use internal rules
Success !
12268 points, 65567 elements
Remove Illegal Elements
Volume Optimization
CombineImprove
ImproveMesh
SplitImprove
ImproveMesh
SwapImprove
SwapImprove2
ImproveMesh
CombineImprove
ImproveMesh
SplitImprove
ImproveMesh
SwapImprove
SwapImprove2
ImproveMesh
CombineImprove
ImproveMesh
SplitImprove
ImproveMesh
SwapImprove
SwapImprove2
ImproveMesh
Update mesh topology
NDOF = 1170736
Update clusters
WARNING: kwarg 'coarsetype' is an undocumented flags option for class <class 'ngsolve.comp.Preconditioner'>, maybe there is a typo?
Create H1AMG
assemble VOL element 54420/54420
call wirebasket preconditioner finalize ( with 9346 free dofs out of 1170736 )
H1AMG: level = 0, num_edges = 58513, nv = 1170736
BlockJacobi Preconditioner, constructor called, #blocks = 4842
BlockJacobi Preconditioner built
H1AMG: level = 1, num_edges = 30950, nv = 4842
BlockJacobi Preconditioner, constructor called, #blocks = 2529
BlockJacobi Preconditioner built
H1AMG: level = 2, num_edges = 16576, nv = 2529
BlockJacobi Preconditioner, constructor called, #blocks = 1328
BlockJacobi Preconditioner built
H1AMG: level = 3, num_edges = 8692, nv = 1328
BlockJacobi Preconditioner, constructor called, #blocks = 696
BlockJacobi Preconditioner built
H1AMG: level = 4, num_edges = 4505, nv = 696
BlockJacobi Preconditioner, constructor called, #blocks = 369
BlockJacobi Preconditioner built
H1AMG: level = 5, num_edges = 2311, nv = 369
BlockJacobi Preconditioner, constructor called, #blocks = 192
BlockJacobi Preconditioner built
H1AMG: level = 6, num_edges = 1133, nv = 192
BlockJacobi Preconditioner, constructor called, #blocks = 100
BlockJacobi Preconditioner built
H1AMG: level = 7, num_edges = 553, nv = 100
BlockJacobi Preconditioner, constructor called, #blocks = 53
BlockJacobi Preconditioner built
H1AMG: level = 8, num_edges = 271, nv = 53
BlockJacobi Preconditioner, constructor called, #blocks = 28
BlockJacobi Preconditioner built
H1AMG: level = 9, num_edges = 126, nv = 28
BlockJacobi Preconditioner, constructor called, #blocks = 15
BlockJacobi Preconditioner built
H1AMG: level = 10, num_edges = 54, nv = 15
BlockJacobi Preconditioner, constructor called, #blocks = 8
BlockJacobi Preconditioner built
has inverse
assemble VOL element 54420/54420
WARNING: maxsteps is deprecated, use maxiter instead!
CG iteration 1, residual = 0.7094090868385201
CG iteration 2, residual = 0.277092354196473
CG iteration 3, residual = 0.2552141476493647
CG iteration 4, residual = 0.29760250572558
CG iteration 5, residual = 0.25515340506459033
CG iteration 6, residual = 0.19409338025273298
CG iteration 7, residual = 0.14466456735602215
CG iteration 8, residual = 0.11216525118555454
CG iteration 9, residual = 0.0795167297866193
CG iteration 10, residual = 0.05885836872647869
CG iteration 11, residual = 0.043432132001021806
CG iteration 12, residual = 0.03576010228039376
CG iteration 13, residual = 0.029804921900339124
CG iteration 14, residual = 0.021364235775509832
CG iteration 15, residual = 0.016395018482029945
CG iteration 16, residual = 0.013065067451515285
CG iteration 17, residual = 0.010281475047778715
CG iteration 18, residual = 0.0075161832386951115
CG iteration 19, residual = 0.005400599104160325
CG iteration 20, residual = 0.004159975246836071
CG iteration 21, residual = 0.0033356715080478648
CG iteration 22, residual = 0.0025567178563386563
CG iteration 23, residual = 0.0018863277812046933
CG iteration 24, residual = 0.0014480171690318302
CG iteration 25, residual = 0.0011583796766805852
CG iteration 26, residual = 0.0009066481187791878
CG iteration 27, residual = 0.0006879506314201771
CG iteration 28, residual = 0.0005269442608123841
CG iteration 29, residual = 0.0004011592733254342
CG iteration 30, residual = 0.0003150350082344221
CG iteration 31, residual = 0.0002498998602943328
CG iteration 32, residual = 0.00019082947428133485
CG iteration 33, residual = 0.0001431514175548389
CG iteration 34, residual = 0.0001117435655230187
CG iteration 35, residual = 8.567914626339054e-05
CG iteration 36, residual = 6.622157865058189e-05
CG iteration 37, residual = 5.077678888471302e-05
CG iteration 38, residual = 3.9347393964067174e-05
CG iteration 39, residual = 3.0699655930232356e-05
CG iteration 40, residual = 2.3329631346555676e-05
CG iteration 41, residual = 1.8101778951878397e-05
CG iteration 42, residual = 1.4422937256375272e-05
CG iteration 43, residual = 1.128070098701103e-05
CG iteration 44, residual = 8.67624883991305e-06
CG iteration 45, residual = 6.472767303048765e-06
CG iteration 46, residual = 5.003440601466715e-06
CG iteration 47, residual = 3.828388670957237e-06
CG iteration 48, residual = 2.928339674985158e-06
CG iteration 49, residual = 2.2656179101175973e-06
CG iteration 50, residual = 1.8273692600402287e-06
CG iteration 51, residual = 1.4226184082012495e-06
CG iteration 52, residual = 1.0818334558222385e-06
CG iteration 53, residual = 8.099502945603005e-07
CG iteration 54, residual = 6.09473074074458e-07
CG iteration 55, residual = 4.6194864798528714e-07
CG iteration 56, residual = 3.571209782788016e-07
CG iteration 57, residual = 2.7591527031657443e-07
CG iteration 58, residual = 2.182412897552229e-07
CG iteration 59, residual = 1.7485809206654988e-07
CG iteration 60, residual = 1.3431990604047457e-07
CG iteration 61, residual = 1.0077397347703597e-07
CG iteration 62, residual = 7.592589306656699e-08
CG iteration 63, residual = 5.952078091484223e-08
CG iteration 64, residual = 4.4861067028682956e-08
CG iteration 65, residual = 3.4204272871611885e-08
CG iteration 66, residual = 2.610924062797616e-08
CG iteration 67, residual = 1.9906599352018196e-08
CG iteration 68, residual = 1.5466948940629167e-08
CG iteration 69, residual = 1.1695566290271218e-08
CG iteration 70, residual = 8.963548384252506e-09
CG iteration 71, residual = 6.810820217702461e-09
CG iteration 72, residual = 5.212600493144689e-09
CG iteration 73, residual = 3.9848212512488375e-09
CG iteration 74, residual = 3.022515412432698e-09
CG iteration 75, residual = 2.299369048826489e-09
CG iteration 76, residual = 1.7707357293575882e-09
CG iteration 77, residual = 1.3495559669023768e-09
CG iteration 78, residual = 1.0254809347208245e-09
CG iteration 79, residual = 7.813152848881661e-10
CG iteration 80, residual = 6.02935469247742e-10
CG iteration 81, residual = 4.5959315327098883e-10
CG iteration 82, residual = 3.4386923428981863e-10
CG iteration 83, residual = 2.6574175505457817e-10
CG iteration 84, residual = 2.0321568056830468e-10
CG iteration 85, residual = 1.559833400122783e-10
CG iteration 86, residual = 1.2007149167737186e-10
CG iteration 87, residual = 9.753844388239724e-11
CG iteration 88, residual = 7.715165931082646e-11
CG iteration 89, residual = 5.86135120487688e-11
CG iteration 90, residual = 4.436208788493557e-11
CG iteration 91, residual = 3.399054505638281e-11
CG iteration 92, residual = 2.5650282759815758e-11
CG iteration 93, residual = 1.9751471755170407e-11
CG iteration 94, residual = 1.5010635692947355e-11
CG iteration 95, residual = 1.1254657180453063e-11
CG iteration 96, residual = 8.697086470015869e-12
CG iteration 97, residual = 6.646105916609159e-12
CG iteration 98, residual = 5.067918150282717e-12
CG iteration 99, residual = 3.791048771937065e-12
CG iteration 100, residual = 2.8942791634958148e-12
CG iteration 101, residual = 2.2093591918667863e-12
CG iteration 102, residual = 1.6751416406460215e-12
CG iteration 103, residual = 1.282319598981103e-12
CG iteration 104, residual = 9.832638543054068e-13
CG iteration 105, residual = 7.67093444418681e-13
CG iteration 106, residual = 6.068687645511326e-13
[9]:
BaseWebGuiScene
Postscript¶
By popular demand, here is the code to draw the figure found at the beginning of this tutorial:
[10]:
from netgen.geom2d import unit_square
mesh = Mesh(unit_square.GenerateMesh(maxh=0.1))
fes_ho = Discontinuous(H1(mesh, order=10))
fes_lo = H1(mesh, order=1, dirichlet=".*")
fes_lam = Discontinuous(H1(mesh, order=1))
fes = FESpace([fes_ho, fes_lo, fes_lam])
uho, ulo, lam = fes.TrialFunction()
a = BilinearForm(fes)
a += Variation(0.5 * grad(uho)*grad(uho)*dx
- 1*uho*dx
+ (uho-ulo)*lam*dx(element_vb=BBND))
gfu = GridFunction(fes)
solvers.Newton(a=a, u=gfu)
Draw(gfu.components[0],deformation=True)
Generate Mesh from spline geometry
Boundary mesh done, np = 40
CalcLocalH: 40 Points 0 Elements 0 Surface Elements
Meshing domain 1 / 1
Surface meshing done
Edgeswapping, topological
Smoothing
Split improve
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Split improve
Combine improve
Smoothing
Edgeswapping, metric
Smoothing
Split improve
Combine improve
Smoothing
Update mesh topology
Newton iteration 0
Update clusters
Assemble linearization
assemble VOL element 232/232
call umfpack ... done
err = 0.39392955469293095
Newton iteration 1
Assemble linearization
assemble VOL element 232/232
call umfpack ... done
err = 1.7898870223932246e-15
[10]:
BaseWebGuiScene
[ ]: