This page was generated from unit-7-optimization/01_Shape_Derivative_Levelset.ipynb.
7.1 Shape optimization via the shape derivative in NGSolve¶
In this tutorial we discuss the implementation of shape optimization algorithms to solve
The analytic solution to this problem is
This problem is solved by fixing an initial guess \(\Omega_0\subset \mathbf{R}^d\) and then considering the problem
where \(X:\mathbf{R}^d \to \mathbf{R}^d\) are (at least) Lipschitz vector fields. We approximate \(X\) by a finite element function.
Initial geometry and shape function¶
- We choose \(f\) as :nbsphinx-math:`begin{equation}
- begin{aligned}
- f(x,y) =& (sqrt{(x - a)^2 + b y^2} - 1) (sqrt{(x + a)^2 + b y^2} - 1) \
&(sqrt{b x^2 + (y - a)^2} - 1) (sqrt{b x^2 + (y + a)^2} - 1) - varepsilon.
end{aligned}
end{equation}` where \(\varepsilon = 0.001, a = 4/5, b = 2\). The corresponding zero level sets of this function are as follows. The green area indicates where \(f\) is negative.
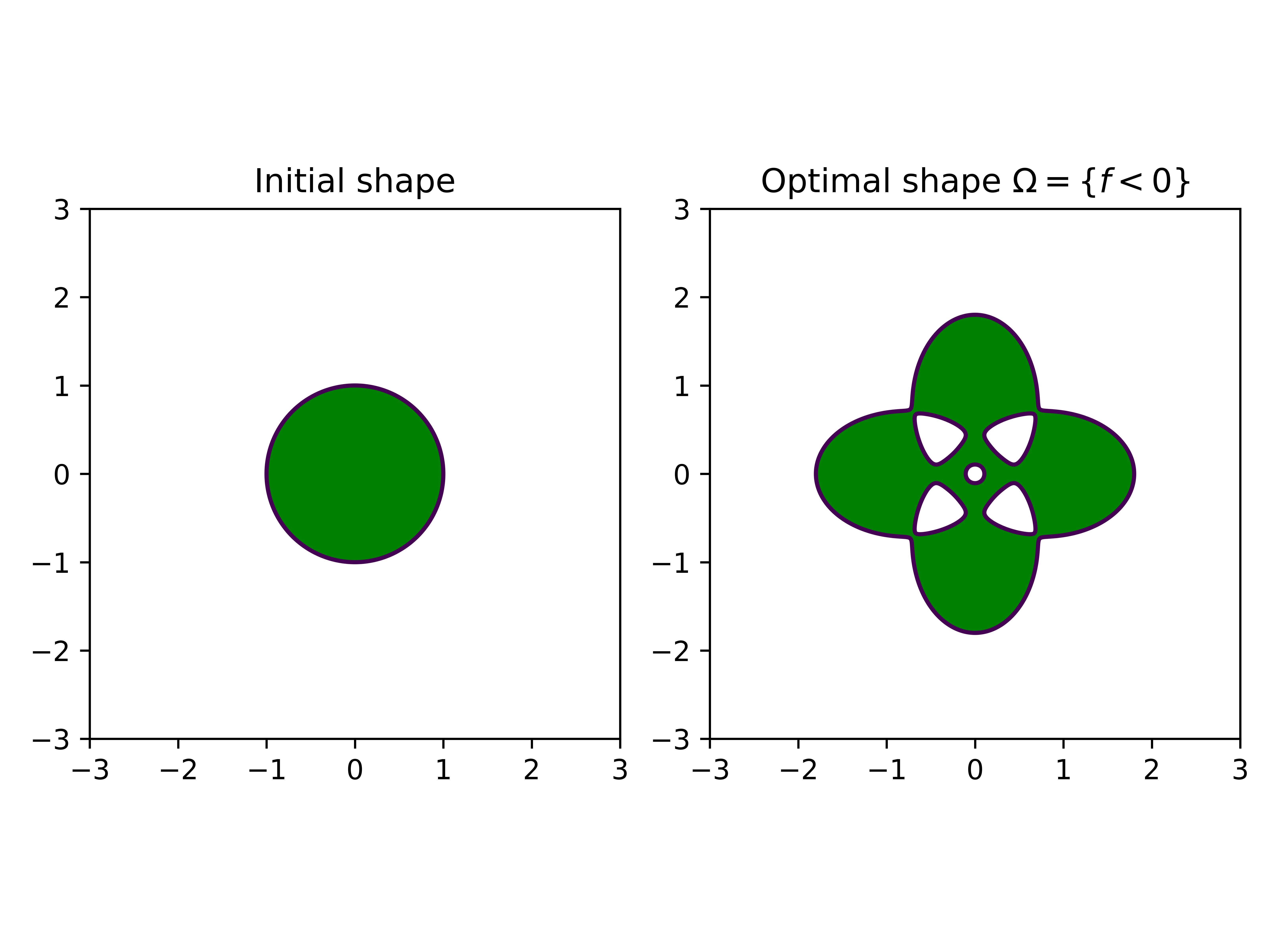
Let us set up the geometry.
[1]:
# Generate the geometry
from ngsolve import *
# load Netgen/NGSolve and start the gui
from ngsolve.webgui import Draw
from netgen.geom2d import SplineGeometry
geo = SplineGeometry()
geo.AddCircle((0,0), r = 2.5)
ngmesh = geo.GenerateMesh(maxh = 0.08)
mesh = Mesh(ngmesh)
mesh.Curve(2)
[1]:
<ngsolve.comp.Mesh at 0x7f03ec3eb130>
[2]:
#gfset.vec[:]=0
#gfset.Set((0.2*x,0))
#mesh.SetDeformation(gfset)
#scene = Draw(gfzero,mesh,"gfset", deformation = gfset)
[3]:
# define the function f and its gradient
a =4.0/5.0
b = 2
f = CoefficientFunction((sqrt((x - a)**2 + b * y**2) - 1) \
* (sqrt((x + a)**2 + b * y**2) - 1) \
* (sqrt(b * x**2 + (y - a)**2) - 1) \
* (sqrt(b * x**2 + (y + a)**2) - 1) - 0.001)
# gradient of f defined as vector valued coefficient function
grad_f = CoefficientFunction((f.Diff(x),f.Diff(y)))
[4]:
# vector space for shape gradient
VEC = H1(mesh, order=1, dim=2)
# grid function for deformation field
gfset = GridFunction(VEC)
gfX = GridFunction(VEC)
Draw(gfset)
[4]:
BaseWebGuiScene
Shape derivative¶
[5]:
# Test and trial functions
PHI, PSI = VEC.TnT()
# shape derivative
dJOmega = LinearForm(VEC)
dJOmega += (div(PSI)*f + InnerProduct(grad_f, PSI) )*dx
Bilinear form¶
to compute the gradient \(X:= \mbox{grad}J(\Omega)\) by
[6]:
# bilinear form for H1 shape gradient; aX represents b_\Omega
aX = BilinearForm(VEC)
aX += InnerProduct(grad(PHI) + grad(PHI).trans, grad(PSI)) * dx
aX += InnerProduct(PHI, PSI) * dx
The first optimisation step¶
Fix an initial domain \(\Omega_0\) and define
Then we have the following relation between the derivative of \(\mathcal J_{\Omega_0}\) and the shape derivative of \(J\):
Here
\((\mbox{id}+X_n)(\Omega_0)\) is current shape
Now we note that \(\varphi \mapsto \varphi\circ(\mbox{id}+X_n)^{-1}\) maps the finite element space on \((\mbox{id}+X_n)(\Omega_0)\) to the finite element space on \(\Omega_0\). Therefore the following are equvalent:
assembling \(\varphi \mapsto D\mathcal J_{\Omega_0}(X_n)(\varphi)\) on the fixed domain \(\Omega_0\)
assembling \(\varphi \mapsto DJ((\mbox{id}+X_n)(\Omega_0))(\varphi)\) on the deformed domain \((\mbox{id}+X_n)(\Omega_0)\).
[7]:
# deform current domain with gfset
mesh.SetDeformation(gfset)
# assemble on deformed domain
aX.Assemble()
dJOmega.Assemble()
mesh.UnsetDeformation()
# unset deformation
Now let’s make one optimization step with step size \(\alpha_1>0\):
[8]:
# compute X_0
gfX.vec.data = aX.mat.Inverse(VEC.FreeDofs(), inverse="sparsecholesky") * dJOmega.vec
print("current cost ", Integrate(f*dx, mesh))
print("Gradient norm ", Norm(gfX.vec))
alpha = 20.0 / Norm(gfX.vec)
gfset.vec[:]=0
scene = Draw(gfset)
# input("A")
gfset.vec.data -= alpha * gfX.vec
mesh.SetDeformation(gfset)
#draw deformed shape
scene.Redraw()
# input("B")
print("cost after gradient step:", Integrate(f, mesh))
mesh.UnsetDeformation()
scene.Redraw()
current cost 63.585440628037816
Gradient norm 445.3891568155293
cost after gradient step: 5.186781651375821
Optimisation loop¶
Now we can set up an optimisation loop. In the second step we compute
by the same procedure as above.
[9]:
import time
iter_max = 50
gfset.vec[:] = 0
mesh.SetDeformation(gfset)
scene = Draw(gfset,mesh,"gfset")
converged = False
alpha =0.11#100.0 / Norm(gfX.vec)
# input("A")
for k in range(iter_max):
mesh.SetDeformation(gfset)
scene.Redraw()
Jold = Integrate(f, mesh)
print("cost at iteration ", k, ': ', Jold)
# assemble bilinear form
aX.Assemble()
# assemble shape derivative
dJOmega.Assemble()
mesh.UnsetDeformation()
gfX.vec.data = aX.mat.Inverse(VEC.FreeDofs(), inverse="sparsecholesky") * dJOmega.vec
# step size control
gfset_old = gfset.vec.CreateVector()
gfset_old.data = gfset.vec
Jnew = Jold + 1
while Jnew > Jold:
gfset.vec.data = gfset_old
gfset.vec.data -= alpha * gfX.vec
mesh.SetDeformation(gfset)
Jnew = Integrate(f, mesh)
mesh.UnsetDeformation()
if Jnew > Jold:
print("reducing step size")
alpha = 0.9*alpha
else:
print("linesearch step accepted")
alpha = alpha*1.5
break
print("step size: ", alpha, '\n')
time.sleep(0.1)
Jold = Jnew
cost at iteration 0 : 63.585440628037816
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.165
cost at iteration 1 : -0.7382612251137118
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.2475
cost at iteration 2 : -0.8176946345276936
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.37124999999999997
cost at iteration 3 : -0.9325865771728552
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.556875
cost at iteration 4 : -1.0701686667161618
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.8353125
cost at iteration 5 : -1.1521943829112362
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.25296875
cost at iteration 6 : -1.1547492098538301
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.52235703125
cost at iteration 7 : -1.1549564604998837
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.4982276723046877
cost at iteration 8 : -1.1550479523538317
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.3270326873287925
cost at iteration 9 : -1.1554541597742467
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.4511102435940346
cost at iteration 10 : -1.155598291044698
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.4281101462330694
cost at iteration 11 : -1.1556276896977924
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.4054746004152756
cost at iteration 12 : -1.1558603169379684
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.3831978279986936
cost at iteration 13 : -1.1559789883243972
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.3612741424249144
cost at iteration 14 : -1.1562105741574882
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.3396979472674797
cost at iteration 15 : -1.156329595403822
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.3184637348032904
cost at iteration 16 : -1.1564431842388996
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.1678094761459925
cost at iteration 17 : -1.156537664168601
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.034369726354171
cost at iteration 18 : -1.1566378011382392
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.0179749661914572
cost at iteration 19 : -1.1566614856496904
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.0018400629773228
cost at iteration 20 : -1.1566888376561855
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.9859608979791321
cost at iteration 21 : -1.156722105821479
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.9703334177461629
cost at iteration 22 : -1.1567606660811283
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.9549536330748863
cost at iteration 23 : -1.1568020235063836
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.9398176179906492
cost at iteration 24 : -1.1568400852839162
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.027690565272775
cost at iteration 25 : -1.1568461070793694
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.0114016698132016
cost at iteration 26 : -1.1568553438714937
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.9953709533466624
cost at iteration 27 : -1.156869963319767
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.9795943237361178
cost at iteration 28 : -1.1568868368878324
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.9640677537049005
cost at iteration 29 : -1.1569064364524482
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.9487872798086778
cost at iteration 30 : -1.1569251064110817
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.0374988904707894
cost at iteration 31 : -1.1569284853084116
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.0210545330568275
cost at iteration 32 : -1.1569330831857187
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.0048708187078768
cost at iteration 33 : -1.1569408837564752
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.988943616231357
cost at iteration 34 : -1.1569499852437595
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.97326885991409
cost at iteration 35 : -1.156961339285066
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.9578425484844518
cost at iteration 36 : -1.1569724959756595
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.047400826767748
cost at iteration 37 : -1.1569741997366239
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.0307995236634793
cost at iteration 38 : -1.156976406299169
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.0144613512134133
cost at iteration 39 : -1.1569809493716794
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.9983821387966807
cost at iteration 40 : -1.1569864477238287
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.9825577818967535
cost at iteration 41 : -1.156994032197216
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.96698424105369
cost at iteration 42 : -1.1570017690359318
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.05739726759221
cost at iteration 43 : -1.1570019192969718
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.0406375209008738
cost at iteration 44 : -1.1570022681885446
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.0241434161945948
cost at iteration 45 : -1.1570046749674276
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 1.0079107430479106
cost at iteration 46 : -1.157008000089275
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.9919353577706012
cost at iteration 47 : -1.157013564226876
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.9762131823499371
cost at iteration 48 : -1.1570196132648598
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.9607402034096908
cost at iteration 49 : -1.1570268476759218
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
reducing step size
linesearch step accepted
step size: 0.9455124711856473
Using SciPy optimize toolbox¶
We use the package scipy.optimize and wrap the shape functions around it.
We first setup the initial geometry as a circle of radius r = 2.5 (as before)
[10]:
# The code in this cell is the same as in the example above.
from ngsolve import *
from ngsolve.webgui import Draw
from netgen.geom2d import SplineGeometry
import numpy as np
ngsglobals.msg_level = 1
geo = SplineGeometry()
geo.AddCircle((0,0), r = 2.5)
ngmesh = geo.GenerateMesh(maxh = 0.08)
mesh = Mesh(ngmesh)
mesh.Curve(2)
# define the function f
a =4.0/5.0
b = 2
f = CoefficientFunction((sqrt((x - a)**2 + b * y**2) - 1) \
* (sqrt((x + a)**2 + b * y**2) - 1) \
* (sqrt(b * x**2 + (y - a)**2) - 1) \
* (sqrt(b * x**2 + (y + a)**2) - 1) - 0.001)
# Now we define the finite element space VEC in which we compute the shape gradient
# element order
order = 1
VEC = H1(mesh, order=order, dim=2)
# define test and trial functions
PHI = VEC.TrialFunction()
PSI = VEC.TestFunction()
# define grid function for deformation of mesh
gfset = GridFunction(VEC)
gfset.Set((0,0))
# only for new gui
#scene = Draw(gfset, mesh, "gfset")
#if scene:
# scene.setDeformation(True)
# plot the mesh and visualise deformation
#Draw(gfset,mesh,"gfset")
#SetVisualization (deformation=True)
Generate Mesh from spline geometry
Curve elements, order = 2
Shape derivative¶
[11]:
fX = LinearForm(VEC)
# analytic shape derivative
fX += f*div(PSI)*dx + (f.Diff(x,PSI[0])) *dx + (f.Diff(y,PSI[1])) *dx
Bilinear form for shape gradient¶
Define the bilinear form
to compute the gradient \(X =: \mbox{grad}J\) by
[12]:
# Cauchy-Riemann descent CR
CR = False
# bilinear form for gradient
aX = BilinearForm(VEC)
aX += InnerProduct(grad(PHI)+grad(PHI).trans, grad(PSI))*dx + InnerProduct(PHI,PSI)*dx
## Cauchy-Riemann regularisation
if CR == True:
gamma = 100
aX += gamma * (PHI.Deriv()[0,0] - PHI.Deriv()[1,1])*(PSI.Deriv()[0,0] - PSI.Deriv()[1,1]) *dx
aX += gamma * (PHI.Deriv()[1,0] + PHI.Deriv()[0,1])*(PSI.Deriv()[1,0] + PSI.Deriv()[0,1]) *dx
aX.Assemble()
invaX = aX.mat.Inverse(VEC.FreeDofs(), inverse="sparsecholesky")
gfX = GridFunction(VEC)
Wrapping the shape function and its gradient¶
Now we define the shape function \(J\) and its gradient grad(J) use the shape derivative \(DJ\). The arguments of \(J\) and grad(J) are vector in \(\mathbf{R}^d\), where \(d\) is the dimension of the finite element space.
[13]:
def J(x_):
gfset.Set((0,0))
# x_ NumPy vector
gfset.vec.FV().NumPy()[:] += x_
mesh.SetDeformation(gfset)
cost_c = Integrate (f, mesh)
mesh.UnsetDeformation()
Redraw(blocking=True)
return cost_c
def gradJ(x_, euclid = False):
gfset.Set((0,0))
# x_ NumPy vector
gfset.vec.FV().NumPy()[:] += x_
mesh.SetDeformation(gfset)
fX.Assemble()
mesh.UnsetDeformation()
if euclid == True:
gfX.vec.data = fX.vec
else:
gfX.vec.data = invaX * fX.vec
return gfX.vec.FV().NumPy().copy()
Gradient descent and Armijo rule¶
We use the functions \(J\) and grad J to define a steepest descent method.We use scipy.optimize.line_search_armijo to compute the step size in each iteration. The Arjmijo rule reads
where \(c_1:= 1e-4\) and \(\alpha_k\) is the step size.
[14]:
# import scipy linesearch method
from scipy.optimize.linesearch import line_search_armijo
def gradient_descent(x0, J_, gradJ_):
xk_ = np.copy(x0)
# maximal iteration
it_max = 50
# count number of function evals
nfval_total = 0
print('\n')
for i in range(1, it_max):
# Compute a step size using a line_search to satisfy the Wolf
# compute shape gradient grad J
grad_xk = gradJ_(xk_,euclid = False)
# compute descent direction
pk = -gradJ_(xk_)
# eval cost function
fold = J_(xk_)
# perform armijo stepsize
if CR == True:
alpha0 = 0.15
else:
alpha0 = 0.11
step, nfval, b = line_search_armijo(J_, xk_, pk = pk, gfk = grad_xk, old_fval = fold, c1=1e-4, alpha0 = alpha0)
nfval_total += nfval
# update the shape and print cost and gradient norm
xk_ = xk_ - step * grad_xk
print('Iteration ', i, '| Cost ', fold, '| grad norm', np.linalg.norm(grad_xk))
mesh.SetDeformation(gfset)
scene.Redraw()
mesh.UnsetDeformation()
if np.linalg.norm(gradJ_(xk_)) < 1e-4:
#print('#######################################')
print('\n'+'{:<20} {:<12} '.format("##################################", ""))
print('{:<20} {:<12} '.format("### success - accuracy reached ###", ""))
print('{:<20} {:<12} '.format("##################################", ""))
print('{:<20} {:<12} '.format("gradient norm: ", np.linalg.norm(gradJ_(xk_))))
print('{:<20} {:<12} '.format("n evals f: ", nfval_total))
print('{:<20} {:<12} '.format("f val: ", fold) + '\n')
break
elif i == it_max-1:
#print('######################################')
print('\n'+'{:<20} {:<12} '.format("#######################", ""))
print('{:<20} {:<12} '.format("### maxiter reached ###", ""))
print('{:<20} {:<12} '.format("#######################", ""))
print('{:<20} {:<12} '.format("gradient norm: ", np.linalg.norm(gradJ_(xk_))))
print('{:<20} {:<12} '.format("n evals f: ", nfval_total))
print('{:<20} {:<12} '.format("f val: ", fold) + '\n')
Now we are ready to run our first optimisation algorithm:¶
[15]:
gfset.vec[:]=0
x0 = gfset.vec.FV().NumPy() # initial guess = 0
scene = Draw(gfset, mesh, "gfset")
gradient_descent(x0, J, gradJ)
Iteration 1 | Cost 63.585440628037816 | grad norm 445.3891568155287
Iteration 2 | Cost -0.7382612251137115 | grad norm 4.83096429660247
Iteration 3 | Cost -0.7857804904180997 | grad norm 4.845836269046255
Iteration 4 | Cost -0.8340190220409043 | grad norm 4.813255015723316
Iteration 5 | Cost -0.8819932057553787 | grad norm 4.724540953421632
Iteration 6 | Cost -0.9285329806179062 | grad norm 4.572725032822891
Iteration 7 | Cost -0.9723683510026829 | grad norm 4.354102519630572
Iteration 8 | Cost -1.012266593262478 | grad norm 4.06994516503022
Iteration 9 | Cost -1.0472020217918228 | grad norm 3.727550452257371
Iteration 10 | Cost -1.0765177275718774 | grad norm 3.34032064494751
Iteration 11 | Cost -1.1000284914205707 | grad norm 2.926603252272237
Iteration 12 | Cost -1.1180257802903903 | grad norm 2.507099966539478
Iteration 13 | Cost -1.131180671798799 | grad norm 2.1019848782671553
Iteration 14 | Cost -1.1403814574777296 | grad norm 1.7276648579607528
Iteration 15 | Cost -1.1465612121108741 | grad norm 1.3952307764340515
Iteration 16 | Cost -1.1505659302990408 | grad norm 1.109999773331136
Iteration 17 | Cost -1.1530834103618983 | grad norm 0.8723292029461809
Iteration 18 | Cost -1.1546273377527376 | grad norm 0.6790431917120955
Iteration 19 | Cost -1.1555564457774934 | grad norm 0.524926205298827
Iteration 20 | Cost -1.1561082962671945 | grad norm 0.4039641213518469
Iteration 21 | Cost -1.156433787972622 | grad norm 0.31020187558462997
Iteration 22 | Cost -1.156625722874324 | grad norm 0.23823684381874635
Iteration 23 | Cost -1.1567397786651876 | grad norm 0.1834369658442347
Iteration 24 | Cost -1.156808743783146 | grad norm 0.14198177265203302
Iteration 25 | Cost -1.1568516663794377 | grad norm 0.11080189179046163
Iteration 26 | Cost -1.1568795063094082 | grad norm 0.08747596157450288
Iteration 27 | Cost -1.1568985323419332 | grad norm 0.07011478242597977
Iteration 28 | Cost -1.1569123209284013 | grad norm 0.057252689443980674
Iteration 29 | Cost -1.1569229144050097 | grad norm 0.047755249097678164
Iteration 30 | Cost -1.1569314851192378 | grad norm 0.0407466320243729
Iteration 31 | Cost -1.1569387130241238 | grad norm 0.03555541402345516
Iteration 32 | Cost -1.1569449993776226 | grad norm 0.03167419925502564
Iteration 33 | Cost -1.1569505871726007 | grad norm 0.028727501046364196
Iteration 34 | Cost -1.1569556288710916 | grad norm 0.02644400443905319
Iteration 35 | Cost -1.156960224537271 | grad norm 0.02463197167974173
Iteration 36 | Cost -1.1569644434456434 | grad norm 0.023158187638717156
Iteration 37 | Cost -1.1569683363413645 | grad norm 0.02193101836093458
Iteration 38 | Cost -1.1569719421945255 | grad norm 0.020887596172047395
Iteration 39 | Cost -1.1569752922488747 | grad norm 0.01998460213096205
Iteration 40 | Cost -1.1569784128384424 | grad norm 0.019192815309508768
Iteration 41 | Cost -1.1569813251680743 | grad norm 0.018489136123896403
Iteration 42 | Cost -1.1569840495535753 | grad norm 0.01785952766202848
Iteration 43 | Cost -1.1569866026100675 | grad norm 0.01729163715015754
Iteration 44 | Cost -1.1569889999341965 | grad norm 0.01677732377711827
Iteration 45 | Cost -1.1569912550705606 | grad norm 0.016310610754291282
Iteration 46 | Cost -1.1569933795428053 | grad norm 0.015884776661851802
Iteration 47 | Cost -1.1569953848027177 | grad norm 0.015496092662886955
Iteration 48 | Cost -1.1569972797142984 | grad norm 0.015138814338987313
Iteration 49 | Cost -1.1569990745698648 | grad norm 0.014816070949413285
#######################
### maxiter reached ###
#######################
gradient norm: 0.014516729693228373
n evals f: 49
f val: -1.1569990745698648
L-BFGS method¶
Now we use the L-BFGS method provided by SciPy. The BFGS method requires the shape function \(J\) and its gradient grad J. We can also specify additional arguments in options, such as maximal iterations and the gradient tolerance.
In the BFGS method we replace
by
- where \(H_\Omega\) is an approximation of the second shape derivative at \(\Omega\). On the discrete level we solve :nbsphinx-math:`begin{align}
- text{ solve }quad B_nX_k & = nabla J(Omega_k) \
& \
- text{ update } quad s_k & := -alpha_k p_k \
y_k & := nabla J_h(Omega_{k+1}) - nabla J_h(Omega_k) \
B_{k+1} &:= B_k + frac{y_kotimes y_k}{y_kcdot s_k} + frac{B_ks_kotimes B_ks_k}{B_ky_kcdot B_ks_k}. end{align}`
[16]:
from scipy.optimize import minimize
x0 = gfset.vec.FV().NumPy()
# options for optimiser
options = {"maxiter":1000,
"disp":True,
"gtol":1e-10}
# we use quasi-Newton method L-BFGS
minimize(J, x0, method='L-BFGS-B', jac=gradJ, options=options)
RUNNING THE L-BFGS-B CODE
* * *
Machine precision = 2.220D-16
N = 7978 M = 10
This problem is unconstrained.
At X0 0 variables are exactly at the bounds
At iterate 0 f= -1.15700D+00 |proj g|= 9.61287D-04
At iterate 1 f= -1.15700D+00 |proj g|= 1.77880D-03
At iterate 2 f= -1.15703D+00 |proj g|= 1.17239D-03
At iterate 3 f= -1.15706D+00 |proj g|= 3.49236D-03
ys=-2.188E-04 -gs= 2.798E-03 BFGS update SKIPPED
At iterate 4 f= -1.15707D+00 |proj g|= 2.35894D-03
At iterate 5 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 9.74156D-04
At iterate 6 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 1.26338D-03
At iterate 7 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 1.33337D-03
At iterate 8 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 1.35435D-03
At iterate 9 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 1.40591D-03
At iterate 10 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 1.42675D-03
At iterate 11 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 1.47314D-03
At iterate 12 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 1.49676D-03
At iterate 13 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 1.53982D-03
At iterate 14 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 1.55132D-03
At iterate 15 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 1.59621D-03
At iterate 16 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 1.61391D-03
At iterate 17 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 1.67265D-03
At iterate 18 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 1.71145D-03
At iterate 19 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 1.81029D-03
At iterate 20 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 1.95316D-03
At iterate 21 f= -1.15709D+00 |proj g|= 1.99807D-03
At iterate 22 f= -1.15711D+00 |proj g|= 1.96615D-03
At iterate 23 f= -1.15712D+00 |proj g|= 1.67698D-03
At iterate 24 f= -1.15712D+00 |proj g|= 2.09128D-04
At iterate 25 f= -1.15712D+00 |proj g|= 1.69140D-04
At iterate 26 f= -1.15712D+00 |proj g|= 1.71713D-04
At iterate 27 f= -1.15713D+00 |proj g|= 2.08134D-04
At iterate 28 f= -1.15713D+00 |proj g|= 2.54162D-04
At iterate 29 f= -1.15713D+00 |proj g|= 1.79445D-04
At iterate 30 f= -1.15713D+00 |proj g|= 1.35263D-04
At iterate 31 f= -1.15713D+00 |proj g|= 1.35263D-04
[16]:
fun: -1.1571274943428573
hess_inv: <7978x7978 LbfgsInvHessProduct with dtype=float64>
jac: array([ 1.10198186e-05, -8.87645210e-05, 4.98921966e-05, ...,
-4.45887814e-06, 5.34733615e-06, -4.57391704e-06])
message: b'CONVERGENCE: REL_REDUCTION_OF_F_<=_FACTR*EPSMCH'
nfev: 219
nit: 31
status: 0
success: True
x: array([-4.75169208e-04, 6.98632778e-01, -6.98685559e-01, ...,
4.72891499e-03, -1.25358955e-03, 4.73507746e-03])
* * *
Tit = total number of iterations
Tnf = total number of function evaluations
Tnint = total number of segments explored during Cauchy searches
Skip = number of BFGS updates skipped
Nact = number of active bounds at final generalized Cauchy point
Projg = norm of the final projected gradient
F = final function value
* * *
N Tit Tnf Tnint Skip Nact Projg F
7978 31 219 1 1 0 1.353D-04 -1.157D+00
F = -1.1571274943428573
CONVERGENCE: REL_REDUCTION_OF_F_<=_FACTR*EPSMCH
Warning: more than 10 function and gradient
evaluations in the last line search. Termination
may possibly be caused by a bad search direction.
Cauchy time 1.450E-04 seconds.
Subspace minimization time 2.740E-02 seconds.
Line search time 5.554E+01 seconds.
Total User time 5.583E+01 seconds.
Improving mesh quality via Cauchy-Riemann equations¶
In the previous section we computed the shape gradient grad J:= X of \(J\) at \(\Omega\) via
This may lead to overly streched or even degenerated triangles. One way to improve this is to modify the above equation by
where
The two equations \(BX = 0\) are precisely the Cauchy-Riemann equations \(-\partial_x X_1 + \partial_y X_2=0\) and \(\partial_y X_1 + \partial_x X_2\). So the bigger \(\gamma\) the more angle preserving is the gradient. So by adding the B term we enforce conformaty with strengh \(\gamma\).
This only means we need to add the \(\alpha\) term to the above bilinear form aX:
[17]:
alpha = 100
aX += alpha * (PHI.Deriv()[0,0] - PHI.Deriv()[1,1])*(PSI.Deriv()[0,0] - PSI.Deriv()[1,1]) *dx
aX += alpha * (PHI.Deriv()[1,0] + PHI.Deriv()[0,1])*(PSI.Deriv()[1,0] + PSI.Deriv()[0,1]) *dx
[ ]: