Adaptive mesh refinement¶
We are solving a stationary heat equation with highly varying coefficients. This example shows how to
- model a 2D geometry be means of line segments
- apply a Zienkiewicz-Zhu type error estimator. The flux is interpolated into an H(div)-conforming finite element space.
- loop over several refinement levels
Download: adaptive.py
from ngsolve import *
from netgen.geom2d import SplineGeometry
# point numbers 0, 1, ... 11
# sub-domain numbers (1), (2), (3)
#
#
# 7-------------6
# | |
# | (2) |
# | |
# 3------4-------------5------2
# | |
# | 11 |
# | / \ |
# | 10 (3) 9 |
# | \ / (1) |
# | 8 |
# | |
# 0---------------------------1
#
def MakeGeometry():
geometry = SplineGeometry()
# point coordinates ...
pnts = [ (0,0), (1,0), (1,0.6), (0,0.6), \
(0.2,0.6), (0.8,0.6), (0.8,0.8), (0.2,0.8), \
(0.5,0.15), (0.65,0.3), (0.5,0.45), (0.35,0.3) ]
pnums = [geometry.AppendPoint(*p) for p in pnts]
# start-point, end-point, boundary-condition, domain on left side, domain on right side:
lines = [ (0,1,1,1,0), (1,2,2,1,0), (2,5,2,1,0), (5,4,2,1,2), (4,3,2,1,0), (3,0,2,1,0), \
(5,6,2,2,0), (6,7,2,2,0), (7,4,2,2,0), \
(8,9,2,3,1), (9,10,2,3,1), (10,11,2,3,1), (11,8,2,3,1) ]
for p1,p2,bc,left,right in lines:
geometry.Append( ["line", pnums[p1], pnums[p2]], bc=bc, leftdomain=left, rightdomain=right)
return geometry
mesh = Mesh(MakeGeometry().GenerateMesh (maxh=0.2))
V = H1(mesh, order=3, dirichlet=[1])
# one heat conductivity coefficient per sub-domain
lam = CoefficientFunction([1, 1000, 10])
a = BilinearForm(V, symmetric=False)
a += Laplace(lam)
# heat-source in sub-domain 3
f = LinearForm(V)
f += Source(CoefficientFunction([0, 0, 1]))
c = Preconditioner(a, type="multigrid", flags= { "inverse" : "sparsecholesky" })
u = GridFunction(V)
# the boundary value problem to be solved on each level
bvp = BVP(bf=a, lf=f, gf=u, pre=c)
# finite element space and gridfunction to represent
# the heatflux:
space_flux = HDiv(mesh, order=2)
gf_flux = GridFunction(space_flux, "flux")
def SolveBVP():
V.Update()
u.Update()
a.Assemble()
f.Assemble()
bvp.Do()
Draw (u)
l = []
def CalcError():
space_flux.Update()
gf_flux.Update()
flux = lam * u.Deriv()
# interpolate finite element flux into H(div) space:
gf_flux.Set (flux)
# Gradient-recovery error estimator
err = 1/lam*(flux-gf_flux)*(flux-gf_flux)
elerr = Integrate (err, mesh, VOL, element_wise=True)
maxerr = max(elerr)
l.append ( (V.ndof, sqrt(sum(elerr)) ))
print ("maxerr = ", maxerr)
for el in mesh.Elements():
mesh.SetRefinementFlag(el, elerr[el.nr] > 0.25*maxerr)
with TaskManager():
while V.ndof < 100000:
SolveBVP()
CalcError()
mesh.Refine()
SolveBVP()
## import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
## plt.yscale('log')
## plt.xscale('log')
## plt.xlabel("ndof")
## plt.ylabel("H1 error-estimate")
## ndof,err = zip(*l)
## plt.plot(ndof,err, "-*")
## plt.ion()
## plt.show()
## input("<press enter to quit>")
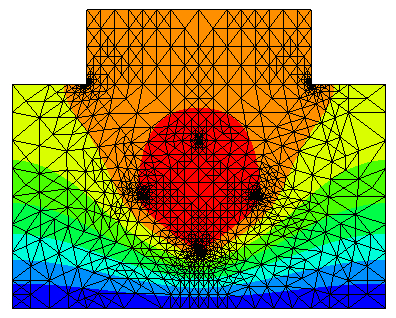
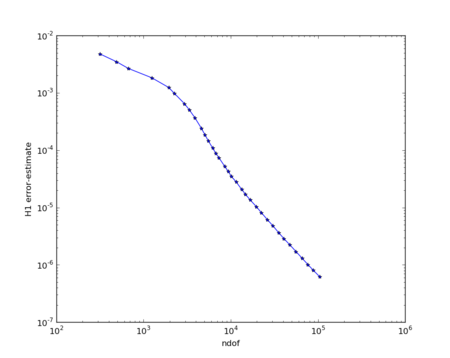
The solution on the adaptively refined mesh, and the convergence plot from matplotlib: