This page was generated from jupyter-files/unit-2.3-hcurlhdiv/hcurlhdiv.ipynb.
2.3 \(H(curl)\) and \(H(div)\) function spaces¶
Scalar and vectorial elements in NGSolve:
Standard continuous \(H^1\) elements:
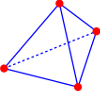
Nedelec’s tangentially-continuous \(H(curl)\)-conforming edge elements:
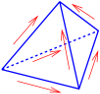
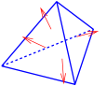
Raviart-Thomas normally-continuous \(H(div)\)-conforming face elements:
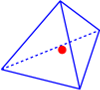
Discontinuous \(L_2\) elements:
These vector-valued spaces allow to represent physical quantities which are either normally or tangentially continuous.
The finite element spaces are related by the de Rham complex:
NGSolve supports these elements of arbitrary order, on all common element shapes (trigs, quads, tets, prisms, pyramids, hexes). Elements may be curved.
[1]:
import netgen.gui
%gui tk
from ngsolve import *
from netgen.geom2d import unit_square
from netgen.csg import unit_cube
mesh = Mesh(unit_square.GenerateMesh(maxh=0.3))
Generate a higher order \(H^1\)-space. We first explore its different types of basis functions.
[2]:
order=3
fes = H1(mesh, order=order)
gfu = GridFunction(fes)
Draw(gfu)
The first #vertices basis functions are hat-functions. By setting the solution vector to a unit-vector, we may look at the individual basis functions:
[3]:
SetVisualization(min=0, max=1)
gfu.vec[:] = 0
# vertex nr:
gfu.vec[17] = 1
Redraw()
The next are edge-bubbles, where we have \((order-1)\) basis functions per edge. A NodeId object refers to a particular vertex, edge, face or cell node in the mesh. We can ask for the degrees of freedom on a node:
[4]:
# basis functions on edge nr:
edge_dofs = fes.GetDofNrs(NodeId(EDGE,10))
print("edge_dofs =", edge_dofs)
SetVisualization(min=-0.05, max=0.05)
gfu.vec[:] = 0
gfu.vec[edge_dofs[0]] = 1
Redraw()
edge_dofs = (44, 45)
Finally, we have \((p-1)(p-2)/2\) inner basis functions on every triangle:
[5]:
trig_dofs = fes.GetDofNrs(NodeId(FACE,0))
print("trig_dofs = ", trig_dofs)
SetVisualization(min=0, max=0.03)
gfu.vec[:] = 0
gfu.vec[trig_dofs[0]] = 1
Redraw()
trig_dofs = (130,)
The FESpace also maintains information about local dofs, interface dofs and wire-basket dofs for the BDDC preconditioner:
[6]:
for i in range(fes.ndof):
print (i,":", fes.CouplingType(i))
0 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
1 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
2 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
3 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
4 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
5 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
6 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
7 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
8 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
9 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
10 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
11 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
12 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
13 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
14 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
15 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
16 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
17 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
18 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
19 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
20 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
21 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
22 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
23 : COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF
24 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
25 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
26 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
27 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
28 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
29 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
30 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
31 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
32 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
33 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
34 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
35 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
36 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
37 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
38 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
39 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
40 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
41 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
42 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
43 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
44 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
45 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
46 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
47 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
48 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
49 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
50 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
51 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
52 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
53 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
54 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
55 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
56 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
57 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
58 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
59 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
60 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
61 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
62 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
63 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
64 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
65 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
66 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
67 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
68 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
69 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
70 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
71 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
72 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
73 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
74 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
75 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
76 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
77 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
78 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
79 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
80 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
81 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
82 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
83 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
84 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
85 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
86 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
87 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
88 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
89 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
90 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
91 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
92 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
93 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
94 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
95 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
96 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
97 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
98 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
99 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
100 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
101 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
102 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
103 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
104 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
105 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
106 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
107 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
108 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
109 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
110 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
111 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
112 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
113 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
114 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
115 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
116 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
117 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
118 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
119 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
120 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
121 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
122 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
123 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
124 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
125 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
126 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
127 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
128 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
129 : COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF
130 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
131 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
132 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
133 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
134 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
135 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
136 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
137 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
138 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
139 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
140 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
141 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
142 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
143 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
144 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
145 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
146 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
147 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
148 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
149 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
150 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
151 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
152 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
153 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
154 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
155 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
156 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
157 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
158 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
159 : COUPLING_TYPE.LOCAL_DOF
\(H(curl)\) finite element space¶
In NGSolve we use hierarchical high order finite element basis functions with node-wise exact sequences. The lowest order space \(W_{l.o}\) is the edge-element space:
where the edge, face and cell blocks are compatible in the sense that
We obtain this by using gradients of \(H^1\) basis functions as \(H(curl)\) basis functions, and some more (see thesis Sabine Zaglmayr):
[7]:
fes = HCurl(mesh, order=2)
uc = GridFunction(fes, name="uc")
Draw (uc)
Draw (curl(uc), mesh, "curl")
[8]:
edge_dofs = fes.GetDofNrs(NodeId(EDGE,10))
print ("edgedofs: ", edge_dofs)
uc.vec[:] = 0
uc.vec[edge_dofs[0]] = 1
Redraw()
edgedofs: (10, 73, 74)
look at them by activating Draw Surface Vectors.
[9]:
face_dofs = fes.GetDofNrs(NodeId(FACE,10))
print ("facedofs: ", face_dofs)
uc.vec[:] = 0
uc.vec[face_dofs[0]] = 1
Redraw()
facedofs: (234, 235, 236)
\(H(div)\) finite element space¶
[10]:
fes = HDiv(mesh, order=2)
ud = GridFunction(fes, name="ud")
Draw (ud)
Draw (div(ud), mesh, "div")
ud.vec[:] = 0
ud.vec[10] = 1
The function spaces know their canonical derivatives. These operations are efficiently implemented by transformation from the reference element.
[11]:
ud.derivname, uc.derivname
[11]:
('div', 'curl')
[12]:
div(uc)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Exception Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-12-3853ecb1c0ea> in <module>()
----> 1 div(uc)
~/gitlab/install/netgen/lib/python3/dist-packages/ngsolve/utils.py in div(func)
82 if add:
83 return add
---> 84 raise Exception("cannot form div")
85
86
Exception: cannot form div
Also the element-wise gradient of H(div) and H(curl) functions is needed for some methods. They are made available by numerical differentiation:
[13]:
print (grad(ud))
coef N6ngcomp31GridFunctionCoefficientFunctionE, real, dims = 2 x 2
we can query the available operators
[14]:
try:
print (ud.Operators())
except:
print ("need newer NGSolve version")
['grad', 'dual']
[ ]: