This page was generated from unit-2.1.4-bddc/bddc.ipynb.
2.1.4 Element-wise BDDC Preconditioner¶
The element-wise BDDC (Balancing Domain Decomposition preconditioner with Constraints) preconditioner in NGSolve is a good general purpose preconditioner that works well both in the shared memory parallel mode as well as in distributed memory mode. In this tutorial, we discuss this preconditioner, related built-in options, and customization from python.
Let us start with a simple description of the element-wise BDDC in the context of Lagrange finite element space \(V\). Here the BDDC preconditioner is constructed on an auxiliary space \(\widetilde{V}\) obtained by connecting only element vertices (leaving edge and face shape functions discontinuous). Although larger, the auxiliary space allows local elimination of edge and face variables. Hence an analogue of the original matrix \(A\) on this space, named \(\widetilde A\), is less expensive to invert. This inverse is used to construct a preconditioner for \(A\) as follows:
Here, \(R\) is the averaging operator for the discontinuous edge and face variables.
To construct a general purpose BDDC preconditioner, NGSolve generalizes this idea to all its finite element spaces by a classification of degrees of freedom. Dofs are classified into (condensable) LOCAL_DOFs that we saw in 1.4 and a remainder that includes these types:
WIREBASKET_DOFINTERFACE_DOFThe original finite element space \(V\) is obtained by requiring conformity of both the above types of dofs, while the auxiliary space \(\widetilde{V}\) is obtained by requiring conformity of WIREBASKET_DOFs only.
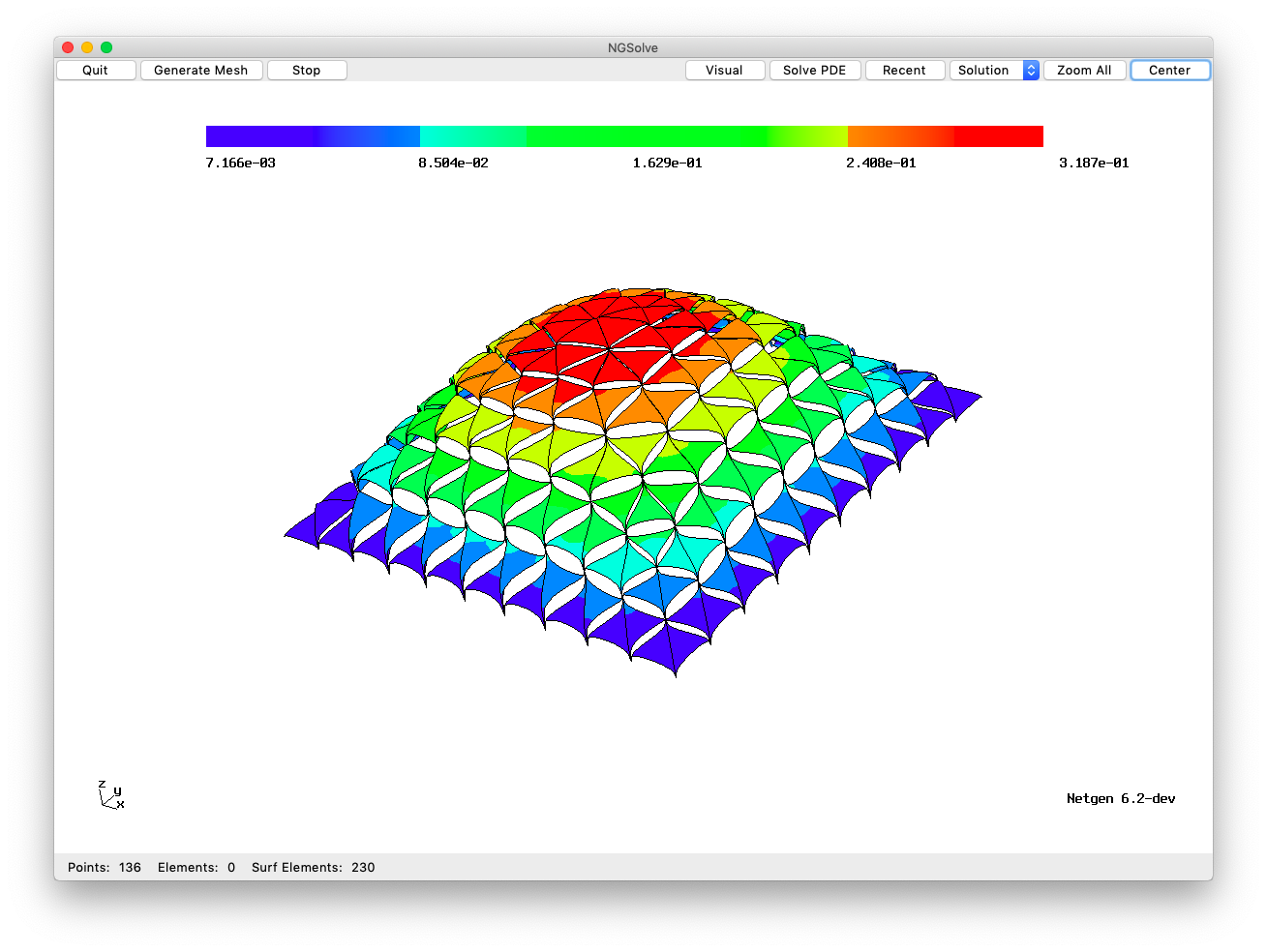
Here is a figure of a typical function in the default \(\widetilde{V}\) (and the code to generate this is at the end of this tutorial) when \(V\) is the Lagrange space:
[1]:
from ngsolve import *
from ngsolve.webgui import Draw
from ngsolve.la import EigenValues_Preconditioner
SetHeapSize(100*1000*1000)
[2]:
mesh = Mesh(unit_cube.GenerateMesh(maxh=0.5))
# mesh = Mesh(unit_square.GenerateMesh(maxh=0.5))
Built-in options¶
Let us define a simple function to study how the spectrum of the preconditioned matrix changes with various options.
Effect of condensation¶
[3]:
def TestPreconditioner (p, condense=False, **args):
fes = H1(mesh, order=p, **args)
u,v = fes.TnT()
a = BilinearForm(fes, eliminate_internal=condense)
a += grad(u)*grad(v)*dx + u*v*dx
c = Preconditioner(a, "bddc")
a.Assemble()
return EigenValues_Preconditioner(a.mat, c.mat)
[4]:
lams = TestPreconditioner(5)
print (lams[0:3], "...\n", lams[-3:])
1.00054
1.03405
1.09891
...
4.48943
4.60085
4.79194
Here is the effect of static condensation on the BDDC preconditioner.
[5]:
lams = TestPreconditioner(5, condense=True)
print (lams[0:3], "...\n", lams[-3:])
1.00023
1.02753
1.08363
...
4.06546
4.12581
4.22957
Tuning the auxiliary space¶
Next, let us study the effect of a few built-in flags for finite element spaces that are useful for tweaking the behavior of the BDDC preconditioner. The effect of these flags varies in two (2D) and three dimensions (3D), e.g.,
wb_fulledges=True: This option keeps all edge-dofs conforming (i.e. they are markedWIREBASKET_DOFs). This option is only meaningful in 3D. If used in 2D, the preconditioner becomes a direct solver.wb_withedges=True: This option keeps only the first edge-dof conforming (i.e., the first edge-dof is markedWIREBASKET_DOFand the remaining edge-dofs are markedINTERFACE_DOFs).
The complete situation is a bit more complex due to the fact these options can take the three values True, False, or Undefined, the two options can be combined, and the space dimension can be 2 or 3. The default value of these flags in NGSolve is Undefined. Here is a table with the summary of the effect of these options:
wb_fulledges |
wb_withedges |
2D |
3D |
|---|---|---|---|
True |
any value |
all |
all |
False/Undefined |
Undefined |
none |
first |
False/Undefined |
False |
none |
none |
False/Undefined |
True |
first |
first |
An entry \(X \in\) {all, none, first} of the last two columns is to be read as follows: \(X\) of the edge-dofs is(are) WIREBASKET_DOF(s).
Here is an example of the effect of one of these flag values.
[6]:
lams = TestPreconditioner(5, condense=True,
wb_withedges=False)
print (lams[0:3], "...\n", lams[-3:])
1.00106
1.07034
1.22031
...
25.4058
25.406
26.9095
Clearly, when moving from the default case (where the first of the edge dofs are wire basket dofs) to the case (where none of the edge dofs are wire basket dofs), the conditioning became less favorable.
Customize¶
From within python, we can change the types of degrees of freedom of finite element spaces, thus affecting the behavior of the BDDC preconditioner.
To depart from the default and commit the first two edge dofs to wire basket, we perform the next steps:
[7]:
fes = H1(mesh, order=10)
u,v = fes.TnT()
for ed in mesh.edges:
dofs = fes.GetDofNrs(ed)
for d in dofs:
fes.SetCouplingType(d, COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF)
# Set the first two edge dofs to be conforming
fes.SetCouplingType(dofs[0], COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF)
fes.SetCouplingType(dofs[1], COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF)
a = BilinearForm(fes, eliminate_internal=True)
a += grad(u)*grad(v)*dx + u*v*dx
c = Preconditioner(a, "bddc")
a.Assemble()
lams=EigenValues_Preconditioner(a.mat, c.mat)
max(lams)/min(lams)
[7]:
9.989385163106073
This is a slight improvement from the default.
[8]:
lams = TestPreconditioner (10, condense=True)
max(lams)/min(lams)
[8]:
13.974958343966291
Combine BDDC with AMG for large problems¶
coarsetype=h1amg flag, we can ask BDDC to replace \({\,\widetilde{A}\,}^{-1}\) by an Algebraic MultiGrid (AMG) preconditioner. Since NGSolve’s h1amg is well-suitedwb_withedges=False to ensure that \(\widetilde{A}\) is made solely with vertex unknowns.[9]:
p = 5
mesh = Mesh(unit_cube.GenerateMesh(maxh=0.05))
fes = H1(mesh, order=p, dirichlet="left|bottom|back",
wb_withedges=False)
print("NDOF = ", fes.ndof)
u,v = fes.TnT()
a = BilinearForm(fes)
a += grad(u)*grad(v)*dx
f = LinearForm(fes)
f += v*dx
with TaskManager():
pre = Preconditioner(a, "bddc", coarsetype="h1amg")
a.Assemble()
f.Assemble()
gfu = GridFunction(fes)
solvers.CG(mat=a.mat, rhs=f.vec, sol=gfu.vec,
pre=pre, maxsteps=500)
Draw(gfu)
NDOF = 839901
WARNING: kwarg 'coarsetype' is an undocumented flags option for class <class 'ngsolve.comp.Preconditioner'>, maybe there is a typo?
CG iteration 1, residual = 0.7217953115360729
CG iteration 2, residual = 0.3050248203792484
CG iteration 3, residual = 0.27490552431422627
CG iteration 4, residual = 0.3254836128333235
CG iteration 5, residual = 0.3197726120226211
CG iteration 6, residual = 0.24005556840618186
CG iteration 7, residual = 0.18373566498596697
CG iteration 8, residual = 0.14887596601780784
CG iteration 9, residual = 0.11776205172130337
CG iteration 10, residual = 0.09415746715001183
CG iteration 11, residual = 0.07003619211581419
CG iteration 12, residual = 0.053374347102851535
CG iteration 13, residual = 0.044173909848494175
CG iteration 14, residual = 0.03617025551380311
CG iteration 15, residual = 0.027632823230957792
CG iteration 16, residual = 0.02169751373422757
CG iteration 17, residual = 0.018137178359608132
CG iteration 18, residual = 0.014942565945605411
CG iteration 19, residual = 0.011867869904081677
CG iteration 20, residual = 0.008882592897356021
CG iteration 21, residual = 0.006862801077328515
CG iteration 22, residual = 0.005164356408633726
CG iteration 23, residual = 0.0039536654098100005
CG iteration 24, residual = 0.003036117884227955
CG iteration 25, residual = 0.002382480626937583
CG iteration 26, residual = 0.0018900134201821149
CG iteration 27, residual = 0.0015173967401730362
CG iteration 28, residual = 0.0011513838097701198
CG iteration 29, residual = 0.0009015669397151677
CG iteration 30, residual = 0.0007164959640586632
CG iteration 31, residual = 0.0005663664655472996
CG iteration 32, residual = 0.00043277283642068174
CG iteration 33, residual = 0.0003353477919847087
CG iteration 34, residual = 0.00026236876368009954
CG iteration 35, residual = 0.00020256510662299034
CG iteration 36, residual = 0.00016357418064306072
CG iteration 37, residual = 0.0001300152298555429
CG iteration 38, residual = 9.827935845585513e-05
CG iteration 39, residual = 7.620034796382225e-05
CG iteration 40, residual = 6.005682339730843e-05
CG iteration 41, residual = 4.736199375005578e-05
CG iteration 42, residual = 3.706921239191699e-05
CG iteration 43, residual = 2.877010949540384e-05
CG iteration 44, residual = 2.225944901974883e-05
CG iteration 45, residual = 1.6972553687842038e-05
CG iteration 46, residual = 1.3339825367753004e-05
CG iteration 47, residual = 1.0603307307925079e-05
CG iteration 48, residual = 8.358155646796e-06
CG iteration 49, residual = 6.421479943617437e-06
CG iteration 50, residual = 5.0015775526173875e-06
CG iteration 51, residual = 3.921761061439456e-06
CG iteration 52, residual = 3.2352034974130787e-06
CG iteration 53, residual = 2.886102005144582e-06
CG iteration 54, residual = 2.112376255003296e-06
CG iteration 55, residual = 1.6606133311676242e-06
CG iteration 56, residual = 1.2837445337772918e-06
CG iteration 57, residual = 9.705184909494672e-07
CG iteration 58, residual = 7.563684637804253e-07
CG iteration 59, residual = 5.900331019696098e-07
CG iteration 60, residual = 4.668470131269099e-07
CG iteration 61, residual = 4.1224804155787495e-07
CG iteration 62, residual = 3.271738144974372e-07
CG iteration 63, residual = 2.4384230901422703e-07
CG iteration 64, residual = 1.8664963988421016e-07
CG iteration 65, residual = 1.4643972766431682e-07
CG iteration 66, residual = 1.1618115436870347e-07
CG iteration 67, residual = 9.563145192357214e-08
CG iteration 68, residual = 8.187320677877167e-08
CG iteration 69, residual = 6.403628048679191e-08
CG iteration 70, residual = 4.867142601932524e-08
CG iteration 71, residual = 3.707626890906999e-08
CG iteration 72, residual = 2.8283680490011095e-08
CG iteration 73, residual = 2.1749737243979445e-08
CG iteration 74, residual = 1.6588069479456357e-08
CG iteration 75, residual = 1.2866509247132231e-08
CG iteration 76, residual = 9.923204081818055e-09
CG iteration 77, residual = 7.687525422291692e-09
CG iteration 78, residual = 5.892097246206354e-09
CG iteration 79, residual = 4.6883879246675374e-09
CG iteration 80, residual = 3.929275808796716e-09
CG iteration 81, residual = 3.182548994258312e-09
CG iteration 82, residual = 2.395366713577637e-09
CG iteration 83, residual = 1.8209201438282208e-09
CG iteration 84, residual = 1.4351800823395052e-09
CG iteration 85, residual = 1.0873309897778853e-09
CG iteration 86, residual = 8.264877942011942e-10
CG iteration 87, residual = 6.490264768003337e-10
CG iteration 88, residual = 5.013849929567815e-10
CG iteration 89, residual = 3.880447189619036e-10
CG iteration 90, residual = 2.9707094190057907e-10
CG iteration 91, residual = 2.2921570840443354e-10
CG iteration 92, residual = 1.9845437534970316e-10
CG iteration 93, residual = 1.736785520084879e-10
CG iteration 94, residual = 1.2387417984403211e-10
CG iteration 95, residual = 9.380276766995558e-11
CG iteration 96, residual = 7.191922299354959e-11
CG iteration 97, residual = 5.5406794493153614e-11
CG iteration 98, residual = 4.312784649916812e-11
CG iteration 99, residual = 3.323867262743906e-11
CG iteration 100, residual = 2.5440289334446467e-11
CG iteration 101, residual = 1.942400789331522e-11
CG iteration 102, residual = 1.5236143606955917e-11
CG iteration 103, residual = 1.2703622245945704e-11
CG iteration 104, residual = 1.0375859635865482e-11
CG iteration 105, residual = 8.180048783277659e-12
CG iteration 106, residual = 6.970287601272701e-12
CG iteration 107, residual = 5.38043660024986e-12
CG iteration 108, residual = 4.073465927613048e-12
CG iteration 109, residual = 3.061112548537294e-12
CG iteration 110, residual = 2.360307421221062e-12
CG iteration 111, residual = 1.8747322147110466e-12
CG iteration 112, residual = 1.6395437456532655e-12
CG iteration 113, residual = 1.3540978757394896e-12
CG iteration 114, residual = 9.767971771535454e-13
CG iteration 115, residual = 7.351702987708824e-13
CG iteration 116, residual = 5.709222941110328e-13
[9]:
BaseWebGuiScene
Postscript¶
By popular demand, here is the code to draw the figure found at the beginning of this tutorial:
[10]:
from netgen.geom2d import unit_square
mesh = Mesh(unit_square.GenerateMesh(maxh=0.1))
fes_ho = Discontinuous(H1(mesh, order=10))
fes_lo = H1(mesh, order=1, dirichlet=".*")
fes_lam = Discontinuous(H1(mesh, order=1))
fes = fes_ho*fes_lo*fes_lam
uho, ulo, lam = fes.TrialFunction()
a = BilinearForm(fes)
a += Variation(0.5 * grad(uho)*grad(uho)*dx
- 1*uho*dx
+ (uho-ulo)*lam*dx(element_vb=BBND))
gfu = GridFunction(fes)
solvers.Newton(a=a, u=gfu)
Draw(gfu.components[0],deformation=True, settings={"camera": {"transformations": [{"type": "rotateX", "angle": -45}]}})
Newton iteration 0
err = 0.39346141669994983
Newton iteration 1
err = 1.8488788182878563e-15
[10]:
BaseWebGuiScene