This page was generated from unit-2.1.3-bddc/bddc.ipynb.
2.1.3 Element-wise BDDC Preconditioner¶
The element-wise BDDC (Balancing Domain Decomposition preconditioner with Constraints) preconditioner in NGSolve is a good general purpose preconditioner that works well both in the shared memory parallel mode as well as in distributed memory mode. In this tutorial, we discuss this preconditioner, related built-in options, and customization from python.
Let us start with a simple description of the element-wise BDDC in the context of Lagrange finite element space \(V\). Here the BDDC preconditoner is constructed on an auxiliary space \(\widetilde{V}\) obtained by connecting only element vertices (leaving edge and face shape functions discontinuous). Although larger, the auxiliary space allows local elimination of edge and face variables. Hence an analogue of the original matrix \(A\) on this space, named \(\widetilde A\), is less expensive to invert. This inverse is used to construct a preconditioner for \(A\) as follows:
Here, \(R\) is the averaging operator for the discontinous edge and face variables.
To construct a general purpose BDDC preconditioner, NGSolve generalizes this idea to all its finite element spaces by a classification of degrees of freedom. Dofs are classified into (condensable) LOCAL_DOFs that we saw in 1.4 and a remainder that includes these types:
WIREBASKET_DOFINTERFACE_DOFThe original finite element space \(V\) is obtained by requiring conformity of both the above types of dofs, while the auxiliary space \(\widetilde{V}\) is obtained by requiring conformity of WIREBASKET_DOFs only.
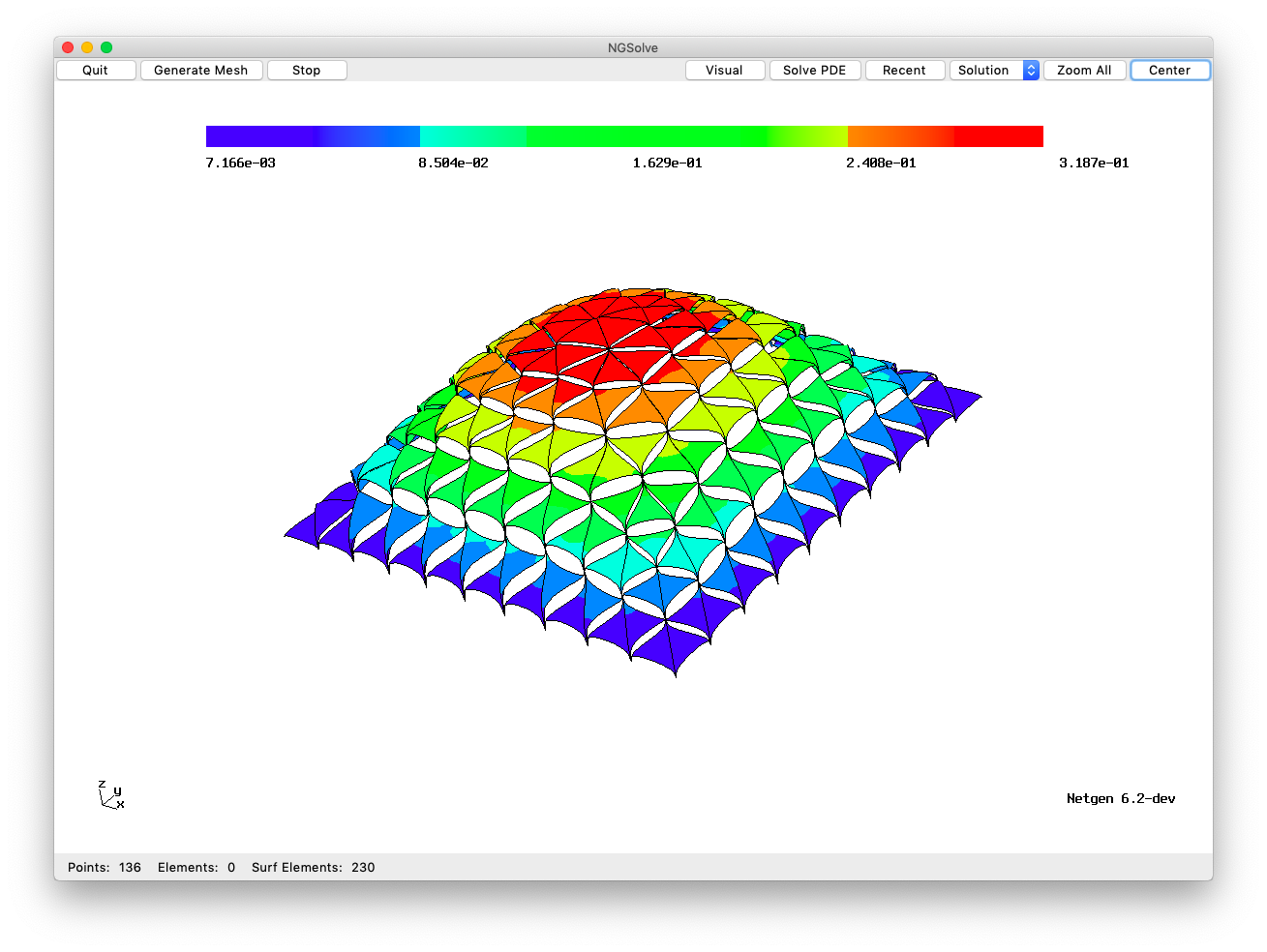
Here is a figure of a typical function in the default \(\widetilde{V}\) (and the code to generate this is at the end of this tutorial) when \(V\) is the Lagrange space:
[1]:
import netgen.gui
from ngsolve import *
from ngsolve.la import EigenValues_Preconditioner
from netgen.csg import unit_cube
from netgen.geom2d import unit_square
SetHeapSize(100*1000*1000)
[2]:
mesh = Mesh(unit_cube.GenerateMesh(maxh=0.5))
# mesh = Mesh(unit_square.GenerateMesh(maxh=0.5))
Built-in options¶
Let us define a simple function to study how the spectrum of the preconditioned matrix changes with various options.
Effect of condensation¶
[3]:
def TestPreconditioner (p, condense=False, **args):
fes = H1(mesh, order=p, **args)
u,v = fes.TnT()
a = BilinearForm(fes, eliminate_internal=condense)
a += grad(u)*grad(v)*dx + u*v*dx
c = Preconditioner(a, "bddc")
a.Assemble()
return EigenValues_Preconditioner(a.mat, c.mat)
[4]:
lams = TestPreconditioner(5)
print (lams[0:3], "...\n", lams[-3:])
1.00234
1.04127
1.13435
...
7.40944
7.63426
7.66348
Here is the effect of static condensation on the BDDC preconditioner.
[5]:
lams = TestPreconditioner(5, condense=True)
print (lams[0:3], "...\n", lams[-3:])
1.00142
1.03925
1.115
...
6.92373
7.01755
7.29845
Tuning the auxiliary space¶
Next, let us study the effect of a few built-in flags for finite element spaces that are useful for tweaking the behavior of the BDDC preconditioner. The effect of these flags varies in two (2D) and three dimensions (3D), e.g.,
wb_fulledges=True: This option keeps all edge-dofs conforming (i.e. they are markedWIREBASKET_DOFs). This option is only meaningful in 3D. If used in 2D, the preconditioner becomes a direct solver.wb_withedges=True: This option keeps only the first edge-dof conforming (i.e., the first edge-dof is markedWIREBASKET_DOFand the remaining edge-dofs are markedINTERFACE_DOFs).
The complete situation is a bit more complex due to the fact these options can take the three values True, False, or Undefined, the two options can be combined, and the space dimension can be 2 or 3. The default value of these flags in NGSolve is Undefined. Here is a table with the summary of the effect of these options:
wb_fulledges |
wb_withedges |
2D |
3D |
|---|---|---|---|
True |
any value |
all |
all |
False/Undefined |
Undefined |
none |
first |
False/Undefined |
False |
none |
none |
False/Undefined |
True |
first |
first |
An entry \(X \in\) {all, none, first} of the last two columns is to be read as follows: \(X\) of the edge-dofs is(are) WIREBASKET_DOF(s).
Here is an example of the effect of one of these flag values.
[6]:
lams = TestPreconditioner(5, condense=True,
wb_withedges=False)
print (lams[0:3], "...\n", lams[-3:])
1.00424
1.09252
1.3257
...
31.0804
33.0369
33.6461
Clearly, when moving from the default case (where the first of the edge dofs are wire basket dofs) to the case (where none of the edge dofs are wire basket dofs), the conditioning became less favorable.
Customize¶
From within python, we can change the types of degrees of freedom of finite element spaces, thus affecting the behavior of the BDDC preconditioner.
To depart from the default and commit the first two edge dofs to wire basket, we perform the next steps:
[7]:
fes = H1(mesh, order=10)
u,v = fes.TnT()
for ed in mesh.edges:
dofs = fes.GetDofNrs(ed)
for d in dofs:
fes.SetCouplingType(d, COUPLING_TYPE.INTERFACE_DOF)
# Set the first two edge dofs to be conforming
fes.SetCouplingType(dofs[0], COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF)
fes.SetCouplingType(dofs[1], COUPLING_TYPE.WIREBASKET_DOF)
a = BilinearForm(fes, eliminate_internal=True)
a += grad(u)*grad(v)*dx + u*v*dx
c = Preconditioner(a, "bddc")
a.Assemble()
lams=EigenValues_Preconditioner(a.mat, c.mat)
max(lams)/min(lams)
[7]:
18.179082265714776
This is a slight improvement from the default.
[8]:
lams = TestPreconditioner (10, condense=True)
max(lams)/min(lams)
[8]:
27.36441706094012
Combine BDDC with AMG for large problems¶
coarsetype=h1amg flag, we can ask BDDC to replace \({\,\widetilde{A}\,}^{-1}\) by an Algebraic MultiGrid (AMG) preconditioner. Since NGSolve’s h1amg is well-suitedwb_withedges=False to ensure that \(\widetilde{A}\) is made solely with vertex unknowns.[9]:
p = 5
mesh = Mesh(unit_cube.GenerateMesh(maxh=0.05))
fes = H1(mesh, order=p, dirichlet="left|bottom|back",
wb_withedges=False)
print("NDOF = ", fes.ndof)
u,v = fes.TnT()
a = BilinearForm(fes)
a += grad(u)*grad(v)*dx
f = LinearForm(fes)
f += v*dx
with TaskManager():
pre = Preconditioner(a, "bddc", coarsetype="h1amg")
a.Assemble()
f.Assemble()
gfu = GridFunction(fes)
solvers.CG(mat=a.mat, rhs=f.vec, sol=gfu.vec,
pre=pre, maxsteps=500)
Draw(gfu)
NDOF = 1165206
iteration 0 error = 0.7051489910244806
iteration 1 error = 0.28021384701734575
iteration 2 error = 0.2631083810280242
iteration 3 error = 0.3090747430601748
iteration 4 error = 0.3164945089710767
iteration 5 error = 0.23137519833634584
iteration 6 error = 0.16940908789440712
iteration 7 error = 0.13859451892079316
iteration 8 error = 0.12062207190616672
iteration 9 error = 0.09053963368459196
iteration 10 error = 0.06109249866045037
iteration 11 error = 0.0481397018523228
iteration 12 error = 0.04137025014573301
iteration 13 error = 0.03652916324949698
iteration 14 error = 0.027339267637011444
iteration 15 error = 0.019687651843194393
iteration 16 error = 0.015329335262383217
iteration 17 error = 0.011824744592549391
iteration 18 error = 0.009647597144193314
iteration 19 error = 0.007086957895098276
iteration 20 error = 0.005179871573650725
iteration 21 error = 0.004032965934753327
iteration 22 error = 0.003117522917661671
iteration 23 error = 0.002437176804548135
iteration 24 error = 0.0018468049516811007
iteration 25 error = 0.0014129821326128594
iteration 26 error = 0.0011095879010380434
iteration 27 error = 0.0008807884942632808
iteration 28 error = 0.0006768163027661401
iteration 29 error = 0.0005176045932742059
iteration 30 error = 0.00039373879396906
iteration 31 error = 0.0003041823923224355
iteration 32 error = 0.0002391703608315311
iteration 33 error = 0.00018576856448505286
iteration 34 error = 0.00014385998852903956
iteration 35 error = 0.00011113996588572277
iteration 36 error = 8.593518185466095e-05
iteration 37 error = 6.71525172207411e-05
iteration 38 error = 5.254131939306249e-05
iteration 39 error = 4.049624637826169e-05
iteration 40 error = 3.147737725659049e-05
iteration 41 error = 2.447172333608955e-05
iteration 42 error = 1.889342906106327e-05
iteration 43 error = 1.5122915977933465e-05
iteration 44 error = 1.2602751982361177e-05
iteration 45 error = 1.1261415646601507e-05
iteration 46 error = 7.885944317954265e-06
iteration 47 error = 5.98839674444583e-06
iteration 48 error = 4.823364815063244e-06
iteration 49 error = 3.7838847420050392e-06
iteration 50 error = 3.273769625873038e-06
iteration 51 error = 2.681028214355873e-06
iteration 52 error = 1.9795694742812375e-06
iteration 53 error = 1.501074364583579e-06
iteration 54 error = 1.216452862275409e-06
iteration 55 error = 1.1008587909546715e-06
iteration 56 error = 7.854976658156464e-07
iteration 57 error = 5.942609413383142e-07
iteration 58 error = 4.545942077915437e-07
iteration 59 error = 3.5710649874640046e-07
iteration 60 error = 2.8150719532443683e-07
iteration 61 error = 2.139120857848269e-07
iteration 62 error = 1.6592967620905575e-07
iteration 63 error = 1.2767480129506756e-07
iteration 64 error = 9.928390580751532e-08
iteration 65 error = 7.867947319461361e-08
iteration 66 error = 6.232252168966511e-08
iteration 67 error = 4.824157260723582e-08
iteration 68 error = 3.666407580023589e-08
iteration 69 error = 2.884795187067263e-08
iteration 70 error = 2.246191672684122e-08
iteration 71 error = 1.7540570122990746e-08
iteration 72 error = 1.3612141351356253e-08
iteration 73 error = 1.041116704168768e-08
iteration 74 error = 8.119585970953112e-09
iteration 75 error = 6.401629661262435e-09
iteration 76 error = 4.872480563347975e-09
iteration 77 error = 3.8310354070277375e-09
iteration 78 error = 2.9573893443828576e-09
iteration 79 error = 2.2752793824545982e-09
iteration 80 error = 1.847621052376332e-09
iteration 81 error = 1.433319928332932e-09
iteration 82 error = 1.1819625569929192e-09
iteration 83 error = 1.057317034187592e-09
iteration 84 error = 7.669403759620004e-10
iteration 85 error = 5.758518323045564e-10
iteration 86 error = 4.3554787440909733e-10
iteration 87 error = 3.4586756983220915e-10
iteration 88 error = 2.776910957583197e-10
iteration 89 error = 2.1322441198396454e-10
iteration 90 error = 1.815555832508962e-10
iteration 91 error = 1.555437295463277e-10
iteration 92 error = 1.1282042814559364e-10
iteration 93 error = 8.385895139776194e-11
iteration 94 error = 6.547005899289998e-11
iteration 95 error = 5.2996396582698844e-11
iteration 96 error = 4.413286827573694e-11
iteration 97 error = 3.719991261139171e-11
iteration 98 error = 2.8047603936731568e-11
iteration 99 error = 2.109095267952922e-11
iteration 100 error = 1.6153592738284807e-11
iteration 101 error = 1.2692091976176826e-11
iteration 102 error = 9.906315473418556e-12
iteration 103 error = 7.687941890110562e-12
iteration 104 error = 5.726009617559662e-12
iteration 105 error = 4.433185566000132e-12
iteration 106 error = 3.4125991467275702e-12
iteration 107 error = 2.59157437949198e-12
iteration 108 error = 2.016488833612046e-12
iteration 109 error = 1.549143811438368e-12
iteration 110 error = 1.2018348242820574e-12
iteration 111 error = 9.683860179787647e-13
iteration 112 error = 7.5823583485474e-13
iteration 113 error = 5.869850533499279e-13
Postscript¶
By popular demand, here is the code to draw the figure found at the beginning of this tutorial:
[10]:
from netgen.geom2d import unit_square
mesh = Mesh(unit_square.GenerateMesh(maxh=0.1))
fes_ho = Discontinuous(H1(mesh, order=10))
fes_lo = H1(mesh, order=1, dirichlet=".*")
fes_lam = Discontinuous(H1(mesh, order=1))
fes = FESpace([fes_ho, fes_lo, fes_lam])
uho, ulo, lam = fes.TrialFunction()
a = BilinearForm(fes)
a += Variation(0.5 * grad(uho)*grad(uho)*dx
- 1*uho*dx
+ (uho-ulo)*lam*dx(element_vb=BBND))
gfu = GridFunction(fes)
solvers.Newton(a=a, u=gfu)
Draw(gfu.components[0])
Newton iteration 0
err = 0.39392955469293095
Newton iteration 1
err = 1.7898870223932246e-15